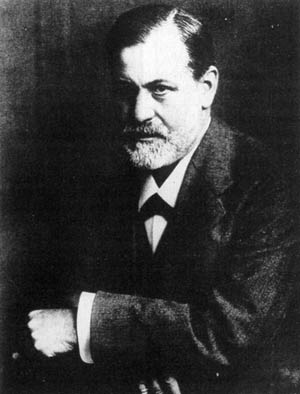Themes And Variations
The Tarzan Novels Of Edgar Rice Burroughs
#5 Tarzan And The Jewels Of Opar
by
R.E. Prindle
Part IV
From Achmet Zek’s Camp To The Recovery Of The Jewels
The nature of the story changes from the departure of Werper and Jane from Achmet Zek’s camp . To that point the story had been developed in a linear fashion. From Zek’s camp on ERB either loses control of his story or changes into an aggregation of scenes between the camp and the Estate leading to the return. Perhaps there is a modification in his psychology.
The struggle for the possession of the jewels and the woman contunues unabated. As always Burroughs tries to construct a story of many surprising twists and turns. This may be an influence of the detective story, Holmes, on him. He may be trying to emulate Doyle.
The problem of who the characters represent in ERB’s life becomes more difficult to determine. Werper continues as ERB’s failed self. I think as relates to Zek and the jewels Zek represents Burroughs’ old sexual competitor, Frank Martin, while Zek, the gold and the Abyssinians represent the deal between McClurg’s and its deal in 1914-15 with A. L. Burt. Burt first had the reprint rights to Tarzan Of The Apes, published in the summer of 1914. Those rights shortly passed to Grossett and Dunlap.
In my estimation Martin never ceased interfering with Burroughs’ marriage at least from 1900 to 1919 when Burroughs fled Chicago. We know that Martin tried to murder Burroughs in 1899 and that his pal, R.S. Patchin, looked up Burroughs in LA after the divorce in 1934 and sent a mocking condolence letter in 1950 when Burroughs died and after Martin had died sometime earlier. Patchin would obviously have been directed by Martin to taunt Burroughs in ’34. It’s clear then that Martin carried a lifelong grudge against Burroughs because of Emma.
Martin is thus portrayed as being in competition with Burroughs in 1914-15 and possibly but probably to a lesser extent in LA.
Jane is shown being captured by Zek twice in the story. Thus Emma was courted or captured by Martin when Burroughs was in Arizona and Idaho. In this story Jane is captured while Tarzan is absent in Opar. The second capture or courting by Martin is diffiicult to pinpoint by the inadequate information at our disposal but following the slender lead offered by the novelist, John Dos Passos, in his novel The Big Money I would think it might be in 1908 when ERB left town for a few weeks or months probably with Dr. Stace. It was of that time that the FDA (Federal Food And Drug Administration) was after Stace for peddling his patent medicines. Burroughs was probably more deeply involved with that than is commonly thought. At any rate his being out of town would have provided an opportunity for Martin. Whether something more current was going on I don’t find improbable but I can’t say.
I would also be interested to learn whether there was any connection between McClurg’s and Martin. Martin was Irish, his father being a railroad executive which explains the private rail car at his disposal, as were, of course, the McClurgs and so was the chief executive Joe Bray. If Martin knew Bray he might have pressured Bray to reject publication of Tarzan doing a quick turnaround when interest was shown by the Cincinatti firm. Martin then might have meddled with Burroughs’ contract with McClurg’s. The contract and McClurg’s attitude is difficult to understand otherwise.
The gold is buried which Zek is supposed to have gotten through Werper, then they have a falling out and Werper is captured by Mourak and his Abyssinians. Mourak would then represent A.L. Burt and a division of the the royalties. If McClurg’s had promoted Tarzan Of The Apes, which they didn’t, Burroughs would have received 10% of 1.30 per copy. Thus at even 100,000 or 200,000 copies he would have received 13,000 or 26.000 dollars. that would have been a good downpayment on his yacht. Martin who must have thought of Burroughs as a hard core loser from his early life would have been incensed by such good fortune that might have placed Burroughs’ income well above his own.
Instead, it doesn’t appear that McClurg’s even printed the whole first edition of 15,000 copies. The book immediately went to A.L. Burt where the price of the book was reduced to 75 or 50 cents with the royalty much reduced to 4 1/2 cents divided fifty-fifty between McClurg’s and Burroughs. It’s hard to believe that ERB wasn’t robbed as he certainly thought he had been. Thus when Mourak unearths the gold he is settling for a portion of the hoard when Zek’s men show up and the battle necessary for the story begins.
In this manner the key issues of gold, jewels and woman are resolved.
So, Werper with the jewels goes in search of Jane to find that she has already fled Zek’s camp. The scenes of the story now take place between the camp, perhaps representing McClurg’s offices and the Estate, representing Burroughs.
The latter half of the book, pages 81-158 in the Ballantine paperback is very condensed in a dream like fashion. The action within the very prescribed area with a multitude of people and incidents is impossible except as a dream story. The appearance of the Belgian officer and askaris must have been photoshopped it is so impossible. In other words, then, the whole last half of the book, if not the whole book, is a dream sequence in which dream logic prevails. I will make an attempt to go into late nineteenth century dream speculation in Part V.
A key point of the story is the regaining of the memory of Tarzan. This occurs near story’s end on page 139 and following. It’s fairly elaborate. In connection with his memory return I would like to point out the manner of his killing the lion when he rescues Jane from Mourak’s boma. The roof fell on Tarzan in imitation of his braining in Toronto while now he picks up a rifle swinging on the rearing lion’s head splintering the stock along with the lion’s skull so that splinters of bone and wood penetrate the brain while the barrel is bent into a V. Rather graphic implying a need for vengeance. Not content with having the roof fall on Tarzan’s head, while trying to escape the Belgian officer an askari lays him out with a crack to the back of the head but ‘he was unhurt.’ One can understand how Raymond Chandler marveled. My head hurts from writing about it. Also Chulk has his head creased by a bullet adding another skull crusher to the story.
The description of the return of Tarzan’s reason seems to fit exactly with Burroughs’ injury. I would have to question whether Burroughs himself didn’t have periods of amnesia. P. 139:
Vaguely the memory of his apish childhood passed slowly in review- then came a strangely tangled mass of faces, figures and events that seemed to have no relation to Tarzan of the Apes, and yet which were, even in this fragmentary form, familiar.
Slowly and painfully recollection was attempting to reassert itself, the hurt brain was mending, as the course of its recent failure to function was being slowly absorbed or removed by the healing process of perfect circulation.
According to medical knowledge of his time the description seems to apply to his own injury. His own blood clot had either just dissolved or was dissolving. Then he says almost in the same manner as in The Girl From Farriss’s:
The people who now passed before his mind’s eye for the first time in weeks were familiar faces; but yet he could neither place them in niches they had once filled in his past life nor call them by name.
In this hazy condition he goes off in search of the She he can’t remember clearly. His memory fully returns as he has Werper by the throat who calls him Lord Greystoke. That and the name John Clayton bring Tarzan fully back to himself. For only a few pages at the end of the book does he have his memory fully recovered.
In order to summarize the rest I have had to outline the actions of the main characters for as with Tarzan and his memory the story is one of ‘a strangely tangled mass of faces, figures and events.’ Whether this is artistry on Burroughs’ part or a dream presentation I am unable to ascertain for certain. Let’s call it artistry.
We will begin with Werper’s activities. While Tarzan promised to retrieve La’s sacred knife Werper appears to no longer have it as it disappears from the story. When Werper escaped from Zek unable to locate Jane he heads East into British territory. He is apprehended by one of Zek’s trackers. On the way back a lion attacks the Arab unhorsing him. Werper mounts the horse riding away directly into the Abyssinian camp of Mourak. Mugambi is captured at the same time. While the troop bathes in a river Mugambi discovers the gems managing to exchange them for river pebbles. Werper tempts Mourak with the story of Tarzan’s gold. While digging the gold they are attacked by Zek and his men. Werper rides off as Mourak is getting the worst of the fight. Zek rides after him. Werper’s horse trips and is too exhausted to rise. Using a device that ERB uses in one of his western novels Werper shoots the horse of the following Zek, crouching behind his own for cover. Zek has lost the woman but now wants the jewels. Werper hasn’t the woman while unknown to himself he neither has the jewels. In exchange for his life he offers Zek the pouch of river stones believing it contained the jewels. Zek accepts. Both men are treacherous. Werper waits to shoot Zek but Zek out foxes him picking up the bag by the drawstring with his rifle barrel from the security of the brush.
Discovering the pebbles he thinks Werper has purposely deceived him stalking down the trail to finish him off. Werper is waiting and pots him with his last shell. As Zek falls the woman, Jane, appears as if by a miracle reuniting the two. Could happen I suppose but definitely in dreams.
So, what are the two men fighting over? The sex interest, as the jewels are involved. Who do Werper and Zek represent? Obviously Burroughs and Martin. The stones are false but as Werper disposes of Zek in the competition for the woman Jane appears as if by magic to run to Werper/ Burroughs with open arms.
Werper with Jane returns to Zek’s camp now under the direction of Zek’s lieutenant, Mohammed Beyd. Rigamarole, then Werper deposits Jane in a tree from whence he expects to retrieve her on the following morning. The next day she is gone.
Werper once again turns East. He is spotted riding along by Tarzan. The Big Guy falls from a tree throwing Werper to the ground demanding to know where his pretty pebbles are. It is at this point Werper recalls Tarzan to his memory by calling him Lord Greystoke. Also at the moment the Belgian officer appears from nowhere, having miraculously ascertained Werper’s whereabouts, to arrest him.
Tarzan wants Werper more than the Belgian so tucking his man under his arm he breaks through the circle of askaris. On the point of success he is brought down from behind. Another thwack on the head. Apparently in a desperate situation Tarzan hears voices from the bush. The Great Apes have their own story line but here it is necessary to introduce them as Tarzan’s saviors. The voice is from Chulk who Tarzan sends after the troop. They attack routing the Africans. In the process Chulk, who is carrying the bound Werper is shot. If you remember Chulk stole the stones from Mugambi, or maybe I haven’t mentioned that yet. Werper falls across him in such a way that his hands bound behind his back come into contact with the pouch. Werper quickly recognizes what the bag contains although he has no idea how the ape came by them.
He then advises Tarzan where he left Jane. The two set out when the furore in Mourak’s camp reaches his ears. ‘Jane might be involved.’ Says Werper. ‘She might.’ says Tarzan telling Werper to wait for him while he checks.
Werper waits not, disappearing into the jungle where his fate awaits him.
Those are the adventures of only one character in this swirling vortex of seventy some pages.
Let’s take Mugambi next as he is the key to the story of the jewels yet plays a minor role. After crawling after Jane and regaining his strength he arrives at Zek’s camp at the same time as Tarzan and Basuli but none are aware of the others. Werper and Jane have already escaped when Tarzen enters the camp to find them missing. Mugambi follows him later also finding both missing. He goes in search of Jane. He walks through the jungle ludicrously calling out ‘Lady’ after each quarter mile or so. Leathern lungs never tiring he shouts Lady into the face of Mourak and is captured. Being a regular lightfoot he escapes having lifted the jewels from Werper. Chulk then lifts them from him, Mugambi disappears until story’s end.
Let’s see: Jane next. Jane along with the jewels is the key to the story. The jewels represent the woman as man’s female treasure. Jane is the eternal woman in that sense. The various men’s attitude toward the jewels reflects their own character. Thus, Tarzan in his amnesiac simplicity wants the jewels for their intrinsic beauty. He rejected the uncut stones for the faceted ones in Opar. Even in the semi darkness of the vaults, or in other words, his ignorance, he perceived the difference.
Werper at various times thinks he can get the gold, the jewels and the woman at once. He is happy to settle for the jewels taking them to his grave. Mourak knowing nothing of the jewels is willing to settle for a few bars of gold. When he takes the woman into his possession it is for the sole purpose of a bribe to his Emperor to mitigate his overall failure. Not at all unreasonable.
Zek is too vile to consider as a human being dying in the fury of losing all. Mugambi and Basuli are happy in their devotion to the woman to whom neither jewels or gold mean anything.
Tarzan then, pure in soul and spirit wins it all, woman, jewels and gold. One is tempted to say he lived happily forever after but, alas, we know the trials ahead of him.
So Jane is carried off to Zek’s camp where all the action is centred while she is there. Both Tarzan and Mugambi show up to rescue her but she has escaped just ahead of Werper who would thus have had the woman and the jewels. Alone in the jungle she once again falls into Zek’s hands- that is to say those of Frank Martin.
Now, Tarzan, who has fallen in with a troop of apes chooses two, Taglat and Chulk, to help him rescue Jane from Zek. Chulk is loyal but Taglat is an old and devious ape, apparently bearing an old grudge against Tarzan, who intends to steal Jane for his own fell purposes much worse than death.
In Tarzan’s attempt to rescue Jane, Taglat succeeds in abducting her. He is in the process of freeing her bonds when a lion leaps on him. In the succeeding battle Jane is able to escape the lion who had just killed Taglat.
Wandering through the jungle she hears shots, the voices of men. Approaching the noise she discover Werper and Zek fighting it out. She climbs a tree behind Werper. When he shoots Zek he hears a heavenly voice from above congratulating him. Jane runs to him hands outstretched. So now Werper has the woman again while believing he can retrieve the jewels. He can’t find them because unbeknownst to him Mugambi had substituted river rocks.
Improbably, except in a dream, he returns to Zek’s camp where he has to solve the problem of Zek’s second in command, Mohammed Beyd. Werper spirits Jane out of the camp but finds her gone the next morning. She had mistaken Mourak and his Abyssinians for Werper. Mourak now in possession of the woman, no gold no jewels, thinks to redeem himself with his Emperor, Menelik II, with this gorgeous female.
During that night’s camp the boma is attacked by hordes of lions. Lions play an amazingly central role in this story. Interestingly this scene is replicated almost exactly in the later Tarzan And The City Of Gold. In Jewels Tarzan rescues a woman while in Gold Tarzan rescues a man. That story’s woman becomes his enemy.
But now Tarzan and Werper hear the tremendous battle with Tarzan entering the boma to rescue Jane. By the time of the rescue Tarzan has regained the woman and the gold but lacks the jewels.
Unless I’m mistaken we now have only Tarzan and the apes to account for.
ERB’s life was at a turning point. At this stage in his career he must have realized that he would have a good annual income for the rest of his life. If only 5000 copies of the first edition of Tarzan of the Apes sold he would have received 6,500.00 Add his magazine sales to that and other income and 1914 must have equaled his income of 1913 or exceeded it. His income probably grew until he was earning c. 100,000 per year for three years from 1919-1922. So he had every reason to believe the world was his oyster through the teens. That must have been an exhilarating feeling. A sense of realization and power must have made him glow. But the period was one of transition, a casting off of the old skin while growing into the new. Thus one sees ERB abandoning his old self -Werper- while attempting to assume the new in Tarzan. Thus in death Werper transfers the jewels, call them the Family Jewels, from himself to Tarzan.
Tarzan begins the novel as an asexual being unaware of what jewels were or their value and receives them a the end of the novel as a release from emasculation or awareness of his sexual prowess. Once again Werper fades in the novel while Tarzan unaware of who he is comes to a full realization. Presumably Burroughs thinks he is able to assume his new role as 1915 ends.
In the novel when Tarzan realizes Werper has stolen the jewels he goes off in search of this symbol of his manhood. Werper is not in Zek’s camp. On the trail Tarzan comes across the dead body of the Arab sent after Werper with he face bitten off. He assumes this is Werper but can’t find the jewels. Wandering about he discovers a troop of apes deciding to run with them for a while. Selecting Chulk and Taglat he goes back to Zek’s camp to rescue Jane. At that point Taglat makes off with Jane. Discovering Zek and Werper on the way to the Estate Tarzan becomes involved in the battle between Zek and Mourak. He sees Zek take the jewels and then throw them to the ground as worthless river rocks.
He encounters Werper in the jungle again and prompted by the man fully regains his memory only to have Werper arrested by the Belgian police officer. The battle between Mourak and the lions ensues. Tarzan goes to rescue Jane, Werper goes to his death.
The unarmed Tarzan faces a rampant lion. Picking up an abandoned rifle he brains the lion, apparently in vengeance for all the indignities and injuries ERB has suffered in life.
Leaping with Jane into a tree they begin the journey back to the Estate to begin life anew. Some time later they come across the bones of Werper to recover the jewels and make the world right.
The novel closes with Tarzan’s exclamation.
“Poor devil!”…Even in death he has made restituion- let his sins lie with his bones.”
Was Burroughs speaking of Werper as his own failed self? I believe sothe latter. Remember that a favorite novel of ERB was Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde and that he believed that every man was two men or had two more or less distinct selves. Human duality is one of the most prominent themes in the corpus; thus ERB himself must have believed that he had a dual personality. Tarzan will have at least two physical doubles, one is Esteban Miranda in Golden Lion and Ant Men, and the other Stanley Obroski in Lion Man. Both were failed men as Werper is here. Both obviously represented the other or early Burroughs as Werper does here.
In killing Werper ERB hoped to eliminate the memory of his failed self as he did with Obroski in Lion Man. In other words escape his emasculation and regain his manhood.
The jumbled and incredibly hard to follow, or at least, remember, last half of the book with its improbable twists and turns in such a compressed manner gives the indication that this is a dream story. Only dream logic makes the story comprehensible if still unbelievable. The story then assumes fairy tale characteristics that don’t have to be probable to be understood as possible.
Can be genius, can be luck. I will examine Burroughs novels in relation to dreams in Part V. This part will not be as comprehensive as I would like but time grows short and it is better to make the attempt as not.
Part V follows.
Tarzan The Untamed
January 3, 2008
Themes And Variations
The Tarzan Novels Of Edgar Rice Burroughs
#7 Tarzan The Untamed
By
R.E. Prindle
Edgar Rice Burroughs seems to be searching for his sexual identity in Tarzan The Untamed. The untamed may refer to the notion that he may be married but Emma has not domesticated the roaring Lion Man.
On my first reading of the novel I merely picked up the surface story, that, to tell the truth, I don’t find very interesting perhaps even implausible and ridiculous. On the second and third readings however the story behind the story, ERB’s psychological dilemma begins to emerge coloring the story with interest.
The story even begins to assume a certain beauty, a poetic shimmer, that takes form as you stare into it. I began to relate Untamed to other novels and stories, that seemed to me to be related and partake of the same dilemma. I don’t know that I can successfully relate them to Untamed but I’ll give it a shot.
For the last few years shifting around in the back of my mind have been the tales of E.T.A. Hoffman. Just a moment ago as I write this I finished another tale of the German romantics, a charming story that I recommend highly, Undine, by Friedrich de la Motte-Fouque. And finally although this may be difficult to see Fyodor Dostoievsky’s Crime and Punishment.
Untamed begins with the murder of Jane, Burroughs aspect of female sexuality, and Tarzan’s killing of the panther or his emasculated sexuality that manifests itself as a homosexual latency.
One then is led to believe that by killing sexual desire Tarzan or ERB believes that he has eliminated the troubling sexual ambivalence of his character. Yet, just a few pages on they flicker to life again in the character of the putative German spy Bertha Kircher. Tarzan first sees Kircher as a woman in the German camp so grasping at the obvious he assumes that she is a German spy. He doesn’t realize and we won’t be told until the end of the story that she is a double agent. In reality she is an English spy posing as a German spy. There’s a complexity there that eludes me at the moment.
She is thus introduced to Tarzan as a woman. The next time he sees her is as a man disguised as a British agent in the English camp. He doesn’t recognize her although he know he has seen him somewhere before. Thus the old sexual ambivalence resurfaces. In what seems to be your standard adventure story delicate psychological nuances begin to flicker around the action story like St. Elmo’s Fire. No matter what the surface story is about the secondary story is about something else.
La Motte Fouque in his Undine also addresses the problem of a man faced with a sexual dilemma that lies within. The path is clear for the hero, Huldbrand, it is only his own weakness that creates the problem for him. In Huldbrand’s case his decision is between two women amidst elemental forces of nature that contrast with the elemental human nature. Undine is a story of astonishing beauty that I can only slaughter in interpreting . I highly recommend you read it. For those deeply into fantasy you will find Undine as fantastic as anything you have ever read; for those into myth and fairytale it is a masterpiece of the kind. Anyone who reads around in this area will have heard it mentioned. I have known of the title for many years but recently in my researches into H.G. Wells it was mentioned that Undine was a favorite of his. I thought it necessary background so I added this gorgeous story to my memory stacks. I should have waited so long; it is a superb Anima-Animus story.
In the December 14th ERBzine George McWhorter provided a list of a few post-WWII books that ERB read. As ERB titles the list, a few of the books he has read, and the list is astonishingly long from a few one can only guess that ERB’s full list must have a couple hundred or more. As reading was a lifelong habit for him and if he consumed titles at that voracious pace then it is truly difficult to guess how many books he read from, say, 1888 to 1910 just before he began writing. Of course his potential list to select from before 1910 was much shorter than ours is today. Titles as obscure today as Undine were relatively well known then. I may be wrong but I pick up hints of Crime and Punishment in ERB’s corpus from time to time. Certainly by his WWII list he had crime on his mind.
We do know that the stories that disappeared into his capacious mind from the period before 1910 gestated for decades in the back of his mind finally finding expression thirty or forty years later. I’m thinking of George W.M. Reynold’s Mysteries Of The Court Of London that burst forth in the 1938 version of The Lad And The Lion. So while I can’t say for certain that ERB read these three authors there is a certain wistfulness and fairy tale quality to the story of Tarzan, Bertha Kircher and Harold Percy Smith-Oldwick that reminds one of the three authors that I have mixed up with Untamed.
So, a woman named Bertalda sends the knight Huldbrand into the elemental forest to prove his love for her. Thus Huldbrand goes to a destiny he never imagined. In the sense of C.G. Jung’s collective unconscious which as I interpret as a set of symbols common to the Western mind, Burroughs also sends Tarzan and his two sexual identities into the elemental jungles of Africa.
La Motte-Fouque invents the water spirit Kuhleborn to forward the action. The presence of so much water indicates that the action takes place in the subconscious of Huldbrand.
Water plays a very different role in Burroughs’ story. In his tale Tarzan braves a watered land to traverse eight very deep and steep ravines that become progressively drier until in the last he almost dies of thirst. As Burroughs’ story covers the four years in his life from late 1914 until mid-1919 one may assume that he had eight bouts of progressively severe depression the eighth and last occurring as he writes his story.
On the other side of the last canyon the well watered jungle begins again. Thus the main story of Tarzan, Bertha and Smith-Oldwick takes place on the edges of the forest and a meadow.
In La Motte-Fouque’s story the elements had set up the conflict from the beginning. As we are told Kuhleborn stole the baby Bertalda away from her parents in an apparent drowning. He then restored a child to the bereaved parents with the child Undine who was actually a water sprite. Bertalda was left by the side of the road where a noble couple found and adopted her. She is the lost daughter of the now aged couple of Undine’s adoptive parents to which Kuhleborn now leads Huldbrand.
Undine’s parents live on an isolated peninsula. As soon as the storm drives Huldbrand to the peninsula the elemental Kuhleborn in the form of a raging torrent turns the peninsula into an island from which there is no escaping. Huldbrand and Undine are thus thrown together. Elemental spirits have no souls. This notion would certainly have had great appeal for Burroughs for whom men without souls was a preoccupation. Undine can only acquire a soul, which she greatly longs for, from the love of a man who has one. She therefore in effect seduces Huldbrand. Kuhleborn disapproves but as to a point Undine’s magic is stronger than his he is reluctantly forced to accede on certain conditions.
A wandering priest is tossed up on shore by Kuhleborn who ties the knot for Undine and Huldbrand. They return to civilization and Berthalda where the conflict between a human woman with a soul and a water sprite without one puts Huldbrand to the test.
So Tarzan who is first associated with Bertha Kircher is once again presented with his emasculation conflict when Smith-Oldwick appears in the picture. The name Smith occurs in Burroughs’ work with some frequency while Old-wick may have sexual connotations unless I’m being too Freudian.
Before Smith-Oldwick does appear Tarzan has to cross the continent from East to West. His wish is to return to his father’s cabin, build an addition or two to make it more roomy and comfortable then settle in as a sort of gentleman farmer. Ah, to be so world weary. And yet that is what Burroughs is about to do.
In a rather remarkable episode Tarzan is crossing Africa when he comes upon Bertha Kircher out there somewhere. He takes her captive but for some unknown reason doesn’t relieve her of the pistol at her side. Even stranger he walks along in front of his captive. Bertha not slow to grasp an opportunity reaches up and lays the butt of her pistol alongside the back of the Big Fella’s head. There’s one bash in the head so far.
Bertha takes off for the railroad leaving Tarzan lying face down in the trail. As he lies Sheeta the panther comes upon him. This presents a sexual problem difficult of analysis. Does it mean that Tarzan is unaware of his attraction to Bertha or what? Tarzan is all but dead as Sheeta prepares to spring on him when who should appear but the Lion whose will Tarzan broke earlier in the story. Now totally devoted to his oppressor he kills Sheeta. Tarzan regains consciousness to find himself nose to nose with Numa. Reminds you of that horrid joke Hillman told a while back about the elephant. In this case it was the same lion.
So the Lion and Tarzan are united in spirit. Tarzan is not yet known as the Lion Man but he will be. In any event the Lion is a guardian spirit for him. In the second book after this one, perhaps reflecting this lion Tarzan will raise and tame the Golden Lion who will be his helpmate and guardian angel. I suspect that the lions Tarzan kills would have been tigers if someone hadn’t objected to the fact that there are no tigers in Africa. In some ways panthers are substitutes for the tiger.
Relieved to find that this lion is his lion Tarzan gets up giving the lion a pat and then trots off down the trail in search of Bertha. In a sort of hobo flashback Bertha finds the train line and hops a freight a few steps ahead of the White Ape. Tarzan misses the connection so we find him forsaking the middle terraces for a trudge down the tracks into town.
I don’t know how many people find these two sequences funny but I do.
Tarzan loses track of Bertha so he begins the long walk to Gabon. Here he has to traverse the eight deep canyons. These canyons have vertical walls while being very deep so that even for the Ape Man these thing become too difficult. Each crevasse gets drier and drier so Tarzan gets weaker and weaker being deprived of, as it were, the feminine water of life. By the time he hits the eighth canyon he is spent. I mean, he has had it. This may be as close to death as the Great Tarmangani has ever come.
He lays down in a manner that indicates he will never get up. The chapter is titled Blood Will Out. A little double entendre. A vulture descends to wait for his meal to die. Instead Tarzan grabs the vulture by the neck sinking his strong white teeth into it throat. Here’s the joke: Blood Will Out. Tarzan’s inherited greatness appears while the vulture’s blood saves his life. Tarzan sucks the vulture dry gaining liquid refreshment while eating the flesh. He now has just enough strength to climb out. He discovers he has crossed the desert and is now in a watered land.
One may assume then that Burroughs has fought off several bouts of severe depression from 1914 to 1919.
Back up on the surface he discover Bertha Kircher in the possession of a Black German trooper. At the same time Smith-Oldwick is flying on a reconnaissance mission when he develops engine trouble landing in a meadow. He whips out his monkey wrench, fixes the problem but before he can take off he is captured by the locals.
Thus he Tarzan and Bertha are brought together. So Tarzan having thought he had resolved his sexual hang-ups at the beginning of the book now learns he hasn’t. The old ambivalence returns in the persons of Bertha and Percy Smith-Oldwick.
In a series of interesting adventures the three Whites are brought together. Tarzan’s male figure falls in love with Bertha. The plane is relocated. An adventure with Usanga the Black German soldier intervenes that is not germane here. Tarzan’s intention is still to go off alone to his father’s cabin so he sees Smith-Oldwick and Bertha off as they begin the flight back to Kenya. Thus we have a second resolution to Burroughs’ sexual dilemma. He packs his sexual problems in a plane and flies them off higher above him than he is high above his daily cares in the trees. He is seen standing in a tree safely above it all watching the plane disappear into the distance. The plane is soaring very high over the tree tops when it takes a dive back to earth. Thus that dream of Burroughs’ getting rid of his ambivalence crashes.
Even this attempt to resolve his sexual dilemma is doomed to failure. He can’t abandon the two so he starts back into the desert from which he almost met his death. His sexual ambivalence has landed in the eighth and most desolate canyon. Undaunted Tarzan returns to near certain death to resolve his problem. The three are in an impossible situation from which it appears that there is no escape.
There he learns that a very unintelligent vulture had apparently mistaken the plane for a dead something. Descending on it the vulture became entangled in the propeller. Never one to lose a chance to bash someone/anyone on the head Burroughs has the bird break a piece of the propeller loose that bashes Smith-Oldwick in the forehead. The bashing definitely establishes Smith-Oldwick as Burroughs’ sexual alter-ego as he presumably now has the same scar on his forehead that both Burroughs and Tarzan sport.
The vulture is an ancient symbol of the mother. One can’t be too sure how aware Burroughs may have been of this but in the Jungian sense of the collective unconscious the symbol would have or may have suggested itself from the common fund. As a student of Africa Burroughs would certainly have had plenty of time to consider vultures especially as his idol Rider Haggard includes vultures in most of his African novels.
If Burroughs is using the vulture as a symbol for his mother that opens the interesting problem of what exactly his relationship to his mother was. First Tarzan strangles, drinks the blood and eats the flesh of the vulture, with perhaps a very sly joke of blood will out, and then the vulture attacks his sexual identity destroying any chance Burroughs may have had of successfully resolving the issue. I merely raise the point.
Having been bashed but not knocked unconscious Smith-Oldwick recovers in time to ease that airplane down. Tarzan arrives but there seems to be no hope of the three leaving the canyon alive.
At this point the residents of the lost civilization of Xuja capture them. Once again not germane to my point here after a series of very interesting hair raising adventures the trio is rescued by some British troops searching for Smith-Oldwick.
Burroughs and Tarzan still have to resolve the sexual dilemma.
The rescue officer advises Tarzan that Jane is not after all dead. This fact apparently resolves the problem for Tarzan. Bertha and Smith-Oldwick return to get married while Tarzan now psychically reunited with Jane returns to East Africa to begin the search for Pal-Ul-Don rather than returning to his father’s cabin.
We don’t know where this leaves Burroughs in August of 1919, more or less the anniversary of the beginning of the Great War in 1914, when he finished the book. We don’t know what his relations with Emma were except that possibly they had reached an accord psychologically.
The story began in Tarzan’s mythical Africa during the War. In the novel the story must take place in 1914-15 but in real life the war ended in November of 1918. This probably coincides with Tarzan drifting off from East Africa back West to Gabon. At the same time in real life Burroughs left Chicago in January 1919 moving West to Los Angeles.
So the village of Usanga in the middle of Africa must represent Chicago. The lost city of Xuja that is located in a desert valley watered by canals brought from a distance must represent the move to LA. So that Burroughs is recording his sexual dilemma and also the move from Chicago to LA against the background of the Great War. Pretty nifty footwork.
He and Emma must have been together as it is very difficult to believe he would have absented himself from her and Tarzana so that this long separation of Tarzan from Jane must represent a mental estrangement from Emma. Perhaps the strain of the move was more than she could bear.
In the next novel Tarzan The Terrible Tarzan makes the long trek to the lost land of Pal-Ul-Don in search of Jane. While the succeeding novel Tarzan And The Golden Lion opens with Jane, Jack and Tarzan returning from Pal-Ul-Don reunited again. At that time there is a distinct coolness between Tarzan and Jane. Whatever reconciliation took place between Emma and Burroughs it was less than satisfactory on Burroughs’ side.
In Golden Lion the two discover a lion cub on the trail that Tarzan takes home to raise as the Golden Lion. The Lion is always cool toward Jane while seeming to protect Tarzan from her. As soon as the lion is mature and trained Tarzan takes off to visit La at Opar. In this instance he and La come close to being a couple while the Golden Lion becomes a close male companion.
Thus Bertha and Smith-Oldwick have turned into La and the Golden Lion. Still unable to resolve his real life problem Burroughs ends Golden Lion by having Tarzan return to Jane. Burroughs has now resolved his emasculation problem by having the Golden Lion as Tarzan’s male buddy. As a beast he is not threat to Burroughs’ masculine identity. The Golden Lion remains Tarzan’s male pal throughout the remaining novels.
Now I have to return to Tarzan The Untamed. This is a very complex novel and I don’t know if I can do it justice.
Part 3 Something Of Value I
October 24, 2007
SOMETHING OF VALUE I, PART III
by
R.E. Prindle
Part 3 of Vol. I.
Freud was severely emasculated in both personal ego and in his group ego. He was in fact a practicing homosexual. His relationship with Fliess was homosexual in nature which Freud confessed vowing never to do it again. His group, the Jews, were and are a severely emasculated people. They have been since they walked away from Ur. But on with Freud.
Freud was fond of telling the story of his father and his hat, it seems that Mr. Freud related a story to Sigmund, or Sigismund as he was known then, (His Hebrew name significantly was Solomon) of how when he was a young man walking down the street proudly wearing his new hat, a gentile knocked the hat from his head into the gutter, snarling: ‘Go get your hat, Jew.’
When Sigmund asked breathlessly what his father did, expecting an heroic response, the old gentleman replied: ‘I stepped into the gutter and picked up my hat.’ severely disappointing the young boy.
Since Freud told and retold this story we may be forgiven for believing it had a profound effect on his young conscious and subconscious minds and possibly his ‘unconscious’ too. On the one hand he may have been so ashamed of his father’s very reasonable reaction that he shared his emasculation encapsulating it in his subconscious as a fixation. It is possible that this story either made or contributed to his homosexuality. On the other hand we know for a fact that it inflamed his group ego with an ardent desire for revenge against the gentiles.
As a result of the story he made the Carthaginian Semite, Hannibal, his alter ego. When Hannibal’s father was defeated by the Romans he had his son swear that the would never cease waging war on the Romans until he died. Obviously Freud made his vow against the Europeans although his father didn’t demand it.
It is no coincidence that both Freud and Hannibal were Semites and that the Romans and Europeans were gentiles. Nor is it a coincidence that both Hannibal and Freud were defeated after seemingly winning the war and that rather than fighting the enemy to the end both fled. Now, it therefore follows that Freud never ceased waging war against the Europeans.
You say: How? Come along. I can’t take you into the Inner Sanctum, which way you will have to find on your own, but I can show you some of the records I have been allowed to abstract from the files.
This will involve the secret history of the human race but don’t be alarmed. If you don’t want to believe it you don’t have to. It still is a rousing good story. Besides, if you should ever come around the archives you’ll find it is true.
Freud himself made an attempt to explain a little of the origins of the Jewish psyche in Inhibitions, Symptoms and Anxiety and Moses And Monotheism. The earlier millennia don’t concern us here. The Jews throughout history in their egotism have felt much put upon. This sense of grievance grew until with the expulsion from Spain after the Reconquest their sense of injustice burst into open flames. The group swore revenge on Europe. It must be remembered that at the end of the thirteenth century they were expelled from England, at the beginning of the fourteenth from France and for the duration, well, they were really welcome nowhere.
They swore to stultify Europe. Judaism is the history of messianism.
Sabbatai Zevi.
This man was the last great messianic imposter. In 1666, the number of the beast plus a thousand, the Jews of Europe awaited the word from Sabbatai, then at the Ottoman Court to begin the slaughter. But Zevi apostatized to Moslemism instead. The uprising never came off. Hung fire. Fizzled.
Hope beats eternal. The learned Rabbis vowed never to place their hopes on a single individual again. They now concocted a plan for the group to rise as one man in rebellion. The date selected for the revolution was the period 1913-28. You want to give yourself a little leeway there. Born in 1856, in 1913 Sigmund Freud was fifty-seven years old. Although none of his biographers say much about his his Jewish background it is quite clear that he was read in Jewish lore. You may say that he wasn’t a religious Jew but he nevertheless was devoutly Jewish.
Freud quite consciously hated the gentiles for personal reasons that meshed quite well into those of his group identity.
During 1913-17 Freud’s reputation was immense both within and without the Jewish community. It was true his heir apparent, C.J. Jung had broken with him perhaps for this very reason but he and Psychoanalytic Movement had suffered no damage.
In psychoanalyis Freud had the means to instruct his group and control the gentiles. It is said that he gave up hypnotism when he turned to psychoanalysis but as a perusal of ‘Group Psychology’ will show he was preparing for a breathtaking attempt at hypnotizing the entire Western world not unlike that of Burroughs’ Lotharians against their invaders.
Freud lived in Vienna where for years, even decades before 1913, emigrating Jews had flowed through from the entry port into Austria from the East of Brody on their way to America via the North German ports. The prosperity of the whole German shipping lines was built on steerage passengers. Nor were the decisions to emigrate necessarily individual; it may have begun that way but to emigrate was soon organized and directed by the international Jewish community. Check the career of Baron Maurice Hirsch.
The Jewish establishments of both Europe and America provided funding. At about this time provisions were made to transport the entire Jewish population of the Pale, from Lithuania to Romania, to the United States Of America. At the time the international Jewish goverment led by Jacob Schiff and Louis Marshall was located in the United States, New York City. The decks were being cleared so as to remove resistance in America. So as not to call too much attention to the fact by having hordes disembark entirely in New York and Boston, for there would be resistance however feeble, the ports of New Orleans and Galveston were organized to deal with millions of immigrants.
This plan was aborted by the Great War. The Jews had already been at war with Russia, or the Czar as they personalized it, for a hundred years. The international Jewish community had engineered the Russo-Japanese war almost pulling off a revolution in its wake in 1905.
Activities were now intensified. At the time and for about the next sixty years the Jews threw a veil of obfuscation over their activities always denying involvement in Communist or Revolutionary matters. In recent years Jewish scholars, for whatever reason, have now found it expedient to admit that which they were accused of but always denied. They now admit that every national subversive Communist part was over fifty percent Jewish. Those of Russia and Germany were considerably higher. Freud had been involved in Jewish subversive organizations like the B’nai B’rith for many years. As the master psychologist, an expert in the unconscious, he prepared the Jewish mind for the great task of the millennial years in Central and Eastern Europe, which would require much bloodshed, while formulating his psychological plan of conquest not dissimilar from the military plans of his hero, Hannibal.
Freud himself was centered in Vienna. A lieutenant, Abraham, was his man in Berlin while Frerenczi was posted to Budapest in Hungary. The three crucial central European points were covered. Jung in Zurich had split off shortly before this. It is interesting that the Jewish psychoanalytic extablishment spitefully denounced him as a Nazi.
The Jewish millennial years began in 1913. The Great War began in 1914. The Bolshevik Revolution occurred in 1917. Freud’s Introductory Lectures On Psychoanalysis appeared in 1917 also, even though there must have been an extreme paper shortage; it is not a short book. Freud encoded last minute instructions to the Revolutionists in the book.
At this point in 1917 Freud released the inhibitions of millions of Mr. Hydes in Russia, Hungary and Germany. The Bolsheviks took Russia out of the war signing a seemingly humiliating peace treat at Brest-Litovsk. As Lenin said the peace treaty was meaningless because it was his intent to stab Germany in the back.
Germany had a huge Communist Party which it is now admitted was around sixty percent Jewish. Now with the United States in the war, Germany debilitated internally and crippled psychologically, thousands of Jewish revolutionaries intent on the realization of the millennium flowed back into Germany from Russia in hopes of achieving the Revolution there, giddy with the hopes of thereby annexing Central and Eastern Europe. That they didn’t was because of the efforts of the German Volkish groups such as Hitler and his Nazi Party.
The unconscious psychoses of the Jewish people who it will be remembered as a group were suffering from severe emasculation were erupting. Emasculation of the Ego is always expressed in a sexual manner frequently sadistic. Freud had been preaching the practice of unrestrained sexual activity for years. Murder is a sexual act. He was against ‘repression’ you remember.
When Russia began its program of expansion under the Romanovs it annexed an enormous number of nationalities. The Russians then tried to impose their language and manners on the conquered peoples in an attempt to form an homogeneous State. In so doing they emasculated the subject peoples. Those same subject peoples were now the masters of the Russians with permission to indulge their ‘unconscious.’
Jews, Letts, Poles and others let loose. Stalin himself was a Georgian.
As Jean Genet correctly saw of the Nazi State, in Russia a criminal intellect was now joined to the political and legal apparatus of the State. The criminal code was changed from an objective one to a subjective one; one of vengeance. For a period of years law was suspended in Russia. Amidst the chaos International Jewish organizations including those of the United States operated openly to coordinate their hopes for the millennium.
What I’m about to say has been denied and suppressed but the example was before both Hitler and Stalin. In Hungary Freud had his man Ferenczi to coordinate the Hungarian Jews. The Jewish Bela Kun (Cohn) seized the government beginning a reign of terror against the gentiles during which thousands of non-Jews were murdered in a horrible sadistic manner commensurate with a severely emasculated Ego.
For some time the Jews had been clamoring for a State of their own. Taking advantage of the chaos in Russia the Jewish American Joint Distribution Committee under the leadership of Schiff and Marshall decided to appropriate the Crimea. Bela Kun who had escaped Hungary during the inevitable reaction, going to Moscow, was sent down to the Crimea to exterminate the population to make lebensraum for the Jews. He was in the process when Lenin died. Stalin then recalled him to Moscow where he was subsequently shot.
All these activities were obscured and suppressed. It is forbidden in American universities to study the subject to this day.
Still, Europe was so horrified that they declined to discuss it or even acknowledge it. But Hitler and Stalin remembered.
The Communists in Moscow being composed solely of emasculated peoples functioning from Freud’s vision of the unconscious like so many Hydes conducted a criminal homosexual style State that would have delighted Genet had he been there. The author the The Thief’s Journal would have gasped at the warehouses full of stolen furs, diamonds and other jewels, art objects and whatever of value that the poor emasculated wretches had stolen from their murdered victims. It was the triumph of the Common Man.
As soon as Stalin gained power he began to discredit and remove Jews from influential positions. Trotsky was sent to a malarial swamp in Siberia to die but from which he escaped to be killed by Stalin’s assasins later. As Stalin consolidated his power he acted more directly until he held the famous show trials of 1936. He then began the systematic elimination of Jews which resulted by the end of 1945 in the death of millions.
Thus Hitler, an emasculated man leading an emasculated people had the Judaeo-Communist example before him. As an avid anti-Communist and open anti-Semite he was virtually isolated by the world that by 1936 was under the control of Judaeo-Communists. He was the antagonist not the protagonist.
While Stalin who had religious training was clever enough to seemingly work through the system openly followed legal controlled methods although the law had been subordinated to his ends. Hitler acted as a homosexual with an ax in his hand. Stalin’s officers dispatched prisoners hidden in the depths of the Lubyanka with a bullet in the back of the head, which method, by the way, was favored by Jewish and Italian members of Organized Crdime in America of the time, while the Nazis brutally beat prisoners, finally shooting them in the back while escaping.
Stalin, Hitler, Freud, which was worse? Freud enabled, Stalin and Hitler executed. They were all the same.
In Russia during the first year or so of Lenin some Russian workers were being read to as they worked. Were they being read the works of Marx or Lenin? No. They were being read the Tarzan novels of Edgar Rice Burrougs. This infuriated the Politburo. The State was trying to impose a collectivist unconscious psychology on the Russians while Burroughs and his great psychological projection were individualist and responsible. In fact, Burroughs offered a concept of the unconscious which was directly opposed to that of Freud. One might say that Burroughs was Dr. Jekyll to Freud’s Mr. Hyde.
Burroughs himself had been severely emasculated at the age of nine. The situation seems to be this: Burroughs came from a prosperous Chicago family. His parents were very proud of their English ancestry. If you’re unwilling to understand national and racial prejudices that were very pronounced at the time then you probably won’t be able to understand. There were strong feelings between the Anglo-Saxon and Celt or English and Irish. The Anglos considered the Celts if not inferior at least eccentric. The Burroughses employed two Irish girls as servants. In all probability Young Burroughs assumed an attitude of superiority which the girls resented. They then concocted a plan to cut young Burroughs down to size.
They had a friend or relative by the name of John who was aged twelve to Burroughs’ nine. Being much larger and tougher than Burroughs he stopped the younger boy on the way to school one day where he thoroughly intimidated and terrified him. It is quite possible that Burroughs messed his pants. In any event, he suffered severe emasculation that was to haunt him all his life. He does not seem to have ever practiced homosexuality although he was haunted by a feeling of sexual ambiguity.
The incident with John the Bully not only played havoc with Burroughs personal psychlogy in the narrow sense of creating a psychosis but there was also an effect in what Freud’s erstwhile associate, C. J. Jung called the collective unconscious. The individual is limited by his very humanity to a small number of general responses.
Thus Burroughs was given a cast of mind which the Hindus denoted as Shivaistic. This is a general outlook or philosophy of life, if you wish, which one adopts unconsciously as the consequence of one’s experience. I share it although it took me nearly a lifetime to recognize and accept it.
Burroughs himself was aware of the fact by at least 1931 when he wrote Tarzan And The Leopard Men. In one key or on one level the story is one of Shiva and Kali his consort. Burroughs names his heroine Kali while she is selected to be the White Goddess of the Leopard Men as part of their death cult.
As can be seen by their complete disregard for life Freud, Hitler and Stalin were also Shivaites.
Shiva and Kali are the Hindu representation of Life and Death. Shiva plays unconcernedly on the pipes while the carnage of life and death goes on around him. The song goes on. Kali, his consort, the goddess of death and regeneration dances on the bodies of the dead to Shiva’s music while wearing a necklace of skulls. Death means nothing because she as the eternal mother has the means to multiply unendingly. Do multitudes die? Why then, multitudes die. Not to worry. Life goes on.
Burroughs also developed an interest in psychology in his attempt to free his mind of the fixation given him by John the Bully. As his psychological notions were well formed by 1911 when he began to write in his attempt to expiate his guilt it follows that he acquired his knowledge during his early married years from 1900 to 1911. He married at 24. He had little opportunity to do his reading before then as the major works were only appearing in the late ’90s.
His main concern was the subconscious mind. While his evolutionary ideas are easier to trace he has left no mention of his psychological reading. It seems certain that he was familiar with FWH Myers who, as noticed, first defined the notion of the unconscious in 1886. He must have read James while Freud’s notions would have been discussed, if not yet translated; thus DH Lawrence had highly developed ideas on the Freudian unconscious in his 1911 Psychoanalysis And The Unconscious while I doubt Burroughs had read Freud in the German.
Also it seems probable that Burroughs had read Le Bon.
Burroughs’ idea of the unconscious differed greatly from Freud’s while being more soundly based in the actual functioning of the mind. While Burroughs’ hero Tarzan seems to function with an integrated personality from his creation in 1911-12 Burroughs himself came very close to integrating his own from 1913 to ’17 or may have although he always had trouble with his Animus and Anima.
Even though Freud advertised the fact that he had taken a year off (golly, a whole year) for self-analysis, whatever the results may have been he never succeeded in integrating his personality or, apparently, realized he should have. He was severely conflicted all his life. Just take a look at his photo where you can see that huge welt running from his lover right cheek across his nose into his forehead. That was caused either by excessive cocaine use or mental conflict in the brain stem, probably both.
As did all mythographers, Burroughs had read his Poe, like them he was concerned with the conscious and subconscious minds. While Stevenson’s Jekyll lost his conscious mind in his subconscious mind, Burroughs cencentrated on the concept of the beast within the man, the relationship between the conscious and the subconscious. In Chapter 3 of The Return Of Tarzan, in what appears to be a plagiarization of the murder scene of Poe’s Murders In The Rue Morgue, Burroughs has Tarzan act out the parts of both the Sailor and the Orang.
Lured up to the apartment on the pretext of helping a young woman, Tarzan is set upon by her accomplices. Discarding the trappings of his recently acquired civilization Tarzan reverts to his anthropoid education of the Jungle becoming Poe’s Orang, yet always retaining the restraints of his humanity or the Sailor.
When the police come he leaps out the window to a telephone pole which one imagines were more common in Chicago than Paris. (Burroughs had never been to Paris so he replicated the urban scene he knew.) While still in his ape guise he has the sense to look down where he sees a policeman below so he climbs up leaping to a rooftop.
Racing across the rooftops of Paris he climbs down another pole. Then in a Hyde-like transformation back to Jekyll he shakes himself from his ape self back into his human self, without the aid of drugs, enters a restaurant to clean up in the rest room then saunter jauntily down the street as though nothing had happened.
Thus the plagiarization of not only Poe but Stevenson was merely an attempt to give a better solution by using the mythological symbols.
Return was written at the end of 1912 and the beginning of 1913.
Burroughs’ own self-analysis would continue through his astonishing output of 1911-17 when he finally integrated his personality with the final volume of his Mucker Trilogy published as the Oakdale Affair but alternately titled Bridge And The Oskaloosa Kid which is the better title. At that time he had exorcised his major fixations which should have integrated his personality.
In understanding that the disintegration of the personality was caused by an affront or affronts to the Ego or Animus that resulted in the creation of fixations that festered in the subconscious that in turn manufactured affects that evidenced themselves in various physical and psychological ways he realized that the same could be exorcised returning the Ego to a whole state.
Unfortunately he strung his theory on through a couple dozen works of fiction disguised as incident. A very few would read all the novels while the only possible interpreters could be those who had read them all not only with a psychological background but an open, inquisitive mind. We’re a very small minority.
If I hadn’t been through the same process on my own I probably never would have recognized it. However as his theories were embodied in his hero Tarzan as mythology they passed into the unconscious of his readers of which, as a teenager, I was one, so shall we say, my mind was prepared.
Part VII Springtime For Edgar Rice Burroughs
October 6, 2007
Springtime For Edgar Rice Burroughs
by
R.E. Prindle
Part VII
The Sequels
The return from San Diego in March-April 1914 was a turning point in Burroughs’ life. In a sense it was a childhood’s end. The past was now the past. ERB’s future lay ahead.
The fact that he had won the gamble of the stay in San Diego being able to spend recklessly and still have his back financially covered must have been a tonic to his self-confidence. He was able to do nearly anything he wanted to do. One was to begin his library. A key book in his library was Edward Gibbon’s Decline And Fall Of The Roman Empire. He recorded its purchase date in 1913 and the day he completed the work just after his birthday in 1915. One imagines that by the time he wrote his three sequels in mid-1914 he had read a few of the volumes of his twelve volume set.
This is important because reading Gibbon is a life changing event. In the language of the sixties the history is consciousness expanding. In a sense it is a transition from childhood to maturity.
It is impossible to stress sufficiently the changes that ERB is going through or the rapidity of the changes. Already just returned from San Diego he is purchasing a new automobile, a Hudson. It is perhaps no coincidence that The Mad King opens with Barney Custer/ERB careening down the road in a new Roadster. That it is gray is of very little significance because the only colors available in 1914 were probably grey and black. Or perhaps as the Hudson appears to be grey in black and white photos Barney’s car for that reason was grey.
One can only imagine the exhilaration ERB experienced as he climbed behind the wheel of big new touring car. It was Hudson not a cheap Ford. Nineteen fourteen was also a turning point in the history of Ford Motors. ERB always disparages Fords in these years proud that he’s driving a more expensive automobile. The woes of not being able to afford a car from 1903 on must have melted away.
Not only did ERB buy a new car but he and his family of wife and three children moved into luxurious new quarters in the affluent Chicago suburb of Oak Park. So ERB began a new life on his return to Chicago.
Shortly after his return Tarzan Of The Apes was released in book form by A.C. McClurg. Magazine and newspaper response to his stories had been terrific so there was no reason for Burroughs not to anticipate large sales. One can imagine him sitting up nights calculating the number. A hundred thousand? Too low. A million? Well, if he got really lucky. We’ve all enjoyed the anticipation of some sort along those lines.
The book was released in May, 1914 but there is no indication that McClurg’s even sold through the fifteen thousand of the contract or, indeed, that they even ever printed that many. The title was turned over to the reprint house of A.L. Burt early the next year in 1915. Burt was so uncertain of the books reception that they made McClurgs guarantee the first printing. When Burt turned the title over to Grossett and Dunlap they claimed to have sold less than seven hundred thousand copies at fifty cents each. Royalties were only four and a half cents a copy of which McClurg’s got half so Burroughs realized a mere pittance.
So what then?
He was thrown back almost wholly on his magazine revenues. He began to receive some money from newspaper syndication but this was relatively a pittance given his expectations. Within a few years movie money would begin coming in but for the time being Burroughs had to keep writing bcause as usual he was spending in advance of receipts.
I believe one can detect a change in the style of his writing at this point.
Whereas prior to the return from San Diego with the energy of the bloom of Spring relying perhaps on stories that had evolved in his mind as he daydreamed in the lean years stories just flowed from his pen. It seems likely that he exhausted that reservoir in San Diego so that now he had actually to work at dreaming up stories. In all three of the titles the sequels are significantly longer than the first halves while changing from personal revelations more toward formal stories.
The editorship of Munsey’s had also changed from Metcalf to Bob Davis- Robert H. Davis. From the available evidence Metcalf seems to have been the more tolerant and indulgent of Burroughs’ writing. When Davis was assigned Burroughs in 1914 the latter was an established star of the Munsey stable of writers. Davis wrote an autobiography c. 1940 that I haven’t been able to obtain but which should have much information on his dealing with ERB.
Davis appears to have been much more critical of Burroughs, even bullying him, pushing suggestions on him that the vulnerable writer couldn’t resist. Davis was the one who suggested that Tarzan have a son something Burroughs always regretted doing. Davis seems to have been of the opinion that ERB used a number of trite situations, situations that have subsequently been amply exploited by the movies. Not having grown up in ERB’s milieu and being sufficienctly underread in the various literatures of the times I am unable to say whether or not Burroughs presentation of Barney Custer’s execution by firing squad was trite or not as Davis states. Why Davis should have accepted the grazing of the head by the bullet that has become so commonplace in the movies and rejected the first episode is beyond me.
That Davis accepted Barney’s escape through the sewer without a demur when the episode is a blatant plagiarism of Jean Valjean’s escape through the sewer in Les Miserables is beyond me also. Burroughs even duplicates the upturned face as the filth rises about Valjean. ERB does provide the original twist of Barney being completely submerged in the sewage. Gruesome enough.
So Davis’ intent seems to have been a contest for control and dominance. It seems then that there were large variations between the magazine stories and the published books as ERB reinserted deleted passages and changed details back to his original writing. Overall, from the available evidence, I hold an unfavorable opinion of Davis’ interference.
On the home front, while ERB may have thought to find acceptance for his success as a writer and his newfound prosperity he was to be bitterly disappointed as his writing was disparaged and his topics made him a literary clown in his contemporaries eyes. To my undertanding he has never been accorded the respect that is his due to this day either in Oak Park or Chicago.
The fact is that he was able to please his audience in the pulp fiction genre mightily not only in 1913-14 but for at least a quarter century until his medium, pulp fiction, began to flounder in the thirties and forties. Having now read so many of his novels four to six times I am beginning now to have a much greater respect for ERB’s writing abilities.
The sequels of all three novels under consideration show an extreme focus on exactly what the story is and told with great economy yet with words so well chosen that the reader learns everything that he has to know. I am especially impressed with the single minded drive of The Mad King.
While obviously desiring acceptance and even importance in Chicago’s society ERB made an effort to be accepted by the newspaper columnists he had so admired from young manhood on. These men were very much admired by ERB. Indeed the columnists occupied a position analogous to the drive time radio commentators of our day. Chicago had some of the best.
Burroughs had collections of Eugene Field and George Ade in his library so that it is clear that he was much influenced by them. He does not seem to have cared for Peter Finley Dunne and his Mr. Dooley Irish dialect stories. Now as man he began to contribute to the successors of Field and Ade. Bert Leston Taylor’s column A Line Of Type Or Two in the Chicago Tribune printed some of Burroughs’ verse submitted under his pseudonym, Normal Bean, as well as another column in the Tribune, In The Wake Of The News by Hugh E. Keogh also known as HEK. (source: Porges) Both columns were prestigious so that the acceptance of ERB’s verse would indicate that it was high enough quality for the columns. After all it isn’t that easy to get into such columns or even have a letter to the editor published. Burroughs also joined the White Paper Club that sounds like a catchall scribblers club. He was ignored and shunned by the prestigious clubs.
A note on cars and then to the books on review. In 1913 he had and sold a Velie. In 1914 he bought and drove a Hudson while he drove a Mitchell in 1915.
The Velie is of interest (see http://www.angelfire.com/mt/velie/ )
The Velie was a low priced model bought second hand so it probably didn’t put ERB out too much. Willard Velie attended Yale at the same time as the Burroughs Boys graduating in 1888. One wonders if the Brothers knew of Velie at Yale. Perhaps such a knowledge may have influenced Burroughs choice or perhaps not.
The choice of the Hudson was undoubtedly influenced by the fact that ERB’s hero, L. Frank Baum, who ERB almost certainly visited in 1913, drove one.
If there is a possible story behind the Mitchell I haven’t learned it as yet. Also it shoud be noted that the movie industry did not affect Baum’s decision to move to Hollywood. Cecil B. Demille and Jesse Lasky didn’t step off the train in LA until 1914 when they introduced Hollywood to the movies.
2.
So now ERB began to organize his life around his future rather than his past. The first burst of writing in which he released his pent up emotions was now spent. On the return to Chicago his writing becomes a vocation in which he had to turn out stories every year for the pulps so that he became a professional writer rather than a quasi-amateur.
Tarzan Of The Apes was published in May upon his return but it would seem to disappointing sales. It was even difficult for McClurg’s to get the reprint firm of A.L. Burt to take it however it did well for Burt although apparently not in the spectacular numbers so often reported. Nevertheless money began to come in from that source.
Burroughs’ writing would also be influenced by the political situation presented by the Wobblies or I.W.W. as well as the outbreak of the Great War in August. That conflict became the subject of the sequel to The Mad King that was written after the war began.
The tone of the three sequels then changed from the first halves becoming less personal in their presentation but still concerned with ERB’s relationship with Emma.
The opening sequence of The Cave Girl-The Mad King-The Eternal Lover was changed to The Cave Man-Sweethearts Primeval (Eternal Lover)-and Barney Custer Of Beatrice (Mad King).
Barney Custer of Beatrice seems to display some first hand knowledge of Bert Weston’s business so it is possible that ERB and family visited Weston and Beatrice on the way back from California. In the only letter in the Weston correspondence near the 1914 date, that of June 14, ERB does not allude to any such visit which may or may not mean anything.
The Cave Man then was written first of the sequels as was The Cave Girl of the original stories. There are very significant elements to the story. ERB would later use the Nadara as the White Goddess in Tarzan And The Leopard Men. That in turn links Nadara to La and thence to Florence. In this story Nadara has been captured by some aborigines and made their goddess as will be Kali Bwana. Just as Nadara was wearing the Panther pelt so Kali Bwana would be associated with the Leopard as goddess of the Leopard Men. So both women are invested with ERB’s symbol of female sexuality.
Just as the long temple here was on a river so would be the Leopard temple. Waldo as Thandar uses the roof as does Tarzan. ERB thus duplicates the story. As Florence entered his life he began to associate her with this early dream of Nadara as well as her successor, La. Signficantly La makes her last appearance in 1930s Tarzan The Invincible transformed to reappear immediately as Kali Bwana of Leopard Men. That would indicate that by 1930 ERB had decided to leave Emma for Florence.
Another interesting twist is the similarity of Nadara and the temple to those of Trader Horn. We know that Trader Horn read Burroughs so it is probable that he somehow picked up a copy of the magazine version of Cave Man gestating the story for a decade or so when it came out of his head in 1927. Thus the close association of Burroughs and Horn before and after the publication of the latter’s story. Keeps getting more and more interesting, doesn’t it?
A second major issue seems to be ERB trying to reconcile himself and his parents. The second half of the Cave Man is very concerned with portraying Thandar/ERB’s father as a fine old man in contrast to the crazy deaf mute of Lad And The Lion. In this story the father figure is sympathetic while the mother figure is more harsh. She does become reconciled to Nadara in the end when she learns the girl is a French Princess. French again. One wonders if ERB’s mother was opposed to his marrying Emma.
Nadara herself who waffles between a representation of Emma/Jane and La in the Cave Girl begins Cave Man as more Ema but becomes morel like La/Kali Bwana as the story progresses ending strongly as the latter which would indicate that ERB already preferred his dream Golden Girl to Emma. He finally settled for the rather commonplace Florence as his version of the Wild Thing.
The story opens with the usual adventures. Getting Nadar back to her people it is necessary to kill King Big Fist to keep her. Thus we have a series of male images that reflect ERB’s conflict with Frank Martin.
Big Fist dead the people appoint Tandar/Waldo as their king. Thandar is in the process of converting the tribe to American Democracy when the earth quake strikes. In addition to head bashing one is astonished at the role earthquakes play in these early stories along with memory loss.
In this one Thandar/Waldo is creating a new society somewhat in imitation of the bizarre improvements Jules Verne made to his Mysterious Island when the earthquake strikes ending Thandar’s experiment.
The earthquake separates him from Nadara who is then pursued by another neanderthal type; perhaps this is a varation on the theme of ERB’s ccontest with marank Martin for Emma’s hand.
In a bizarre episode Thandar puts to sea in a bobbing strange little boat finally falling in with Pirates. From then on the story resembles Pirate Blood. Pirate Blood appeared at the same time as his relationship with Florence developed so the two are proable related to his Anima fantasies.
All comes out right in the end as the Pirates restore the belongings of Waldo’s father and mother whose yacht they had captured. Thandar rescues Nadara, all are reunited and Thandar/Waldo and Nadara are able to consummate their natural union with the marriage rites of civilization. An odd little story overall.
ERB next turned to the sequel of The Eternal Lover, Sweethearts Primeval. I just like this story. Nu and Victoria return to the Niocene. ERB missed some opportunities here. While Nu left the Niocene to go to the present Nat-ul never did. So when Victoria made her first trip to the Niocene both she and Nat-Ul should have been there. It would have been well if ERB had explained how their two being meshed after the munerous rebirths of Nat-Ul that produced Victoria.
In this story Nat-Ul who is a variation of La, and Nu become separated. The story is their attempt to reunite. Once again a character who may represent Frank Martin attempts to abduct Nat-Ul but she escapes him to fall into the clutches of another cave man only to escape finding her way to a small island.
The imagery is quite wonderful. Burroughs at his best. The scenery is quite reminiscent of Pellucidar with its coasts and islands. The pirate theme is also prominent in the Pellucidar stories of this time.
Nat-Ul manages to be abducted a number of times escaping each time.
Nu is hampered in his search for Nat-Ul by the appearance of a woman named Gron the wife of Tur of the Boat People. She attches herself to Num who has a difficult time getting rid of her. In the end Nu goes off in seach of the tiger OO this time dying while Victoria/Nat-Ul returns to the present leaving a hole in Space and Time.
In the end we learn that the whole story of Nu took place in the three mintues Victoria was unconcious.
Burroughs then turned to the sequel of The Mad King. The reversal in sequence of The Mad King and The Eternal Lover was necessitated by the fact that after the first part of The Mad King Barney had gone to Africa so that it was now necessary to get him back to Lutha.
Thus the Mad King and The Eternal Lover are actually one novel of the History of Barney Custer. The two books could be combined and titled something like The Adventures Of Barney Custer in Lutha and Africa.
The proper way to read the two books then is Part I of The Mad King, both parts of The Eternal Lover and then the sequel to The Mad King.
After losing Emma in Mad King Part I, Barney goes to Africa to ‘forget’ along with Butzow. Leaving Africa we next find him and Butzow in Beatrice, Nebraska visiting Bert and Margaret and their grain mill.
If Peter of Bletz had lost rack of Barney in Africa he relocates him in Beatrice (I am informed that Beatrice if pronounced Be-at-trice). After a failed murder attempt by Peter’s henchman Maenck Barney and Butzow return to Lutha.
As the story was written after the beginning of the Great War Austria is now attempting to annex Lutha. Apparently ERB was opposed to Austria as he sides with the Serbs.
Having been unable to forget Emma in Africa Barney now attempts to win her hand from King Leopold.
Barney and Leopold are yet another variation on The Prince And The Pauper then. Barney is captured trying to enter Lutha and put before a firing squad. Miraculously escaping death he escapes the Austrians by a direct borrowing of Jean Valjean’s escape through the sewers of Paris.
He is temporarily reunited with Emma but then captured by Maenck. Taken to Leopold he is sentenced to death but contrives to escape by exchanging identities with Leopold. In the guise of Leopold Barney manages to save Lutha from the Austrians. He dressed in Royal and Leopold dressed in rages the two are impossible to tell apart which replicates Twain’s story.
Barney is more seriously injured than Leiop[old so more vulnerable and also stupidly trusting. It should be clear that Barney and Leopold are doppelgangers of ERB. The crux of the problme here is the struggle for Emma. She had been promised in marriage to Leopold so that she is unwilling to disengage fromt he agreement without Leopold’s consent.
ERB writes this remarkable passage about his tow identities, the one the loser of yesteryear, Leopold, and the other the success of his present, Barney.
Quote:
‘What do you intend doing with me?” (Leopold) said. “Are you going to keep your word and return my identity?”
“I have promised,” replied Barney, “and what I promise I always perform.”
“Then exchange clothing with me at once,” cried the king, half rising from his cot.
‘Not so fast, my friend,” replied the American. “There are a few trifling details to be arranged before we resume our proper personalities.”
Unquote.
One of the trifling details is the release of Emma from her obligation to Leopold. Barney extorts the letter releasing the king placing it under his pillow. Exhausted from his wound he then falls asleep. Not so tired Leopold waits until Barney is asleep than recovers his clothes takes back the letter and leaves Barney to his fate.
Up to this point in 1913-14’s output ERB has been struggling to make amends with for his dismal performance in the first thirteen yers of marriage and regain her confidence. Thus Leopold represents the old ERB and Barney the new. As Emma has been married to ERB and is familiar with his loser persona it is difficult for her to transit from Leopold to Barney in her affections. As they are so similar in appearance she had difficulty telling them apart. This has been ERB;s dilemma for the last year and a half, convincing Emma that he is trustworthy and will continue to be a good provider.
ERB has confidence in his ability to continue his writing and finanical success but his future was not so clear to Emma as he continued his wastrel ways. As she could not share his optimism she continued to be wary refusing to accord him the trust and actually the respect he desired.
Leopold in possession of the letter identifying him as Barney races to Lustadt presumably with the intent to present Emma with the letter identifying him as Barney, the man she really wants, the marrying her quickly under the false pretense thus foiling Barney.
His own plan is foiled when upon arriving at the castle in Lustadt he is shot dead by Maenck who mistakes him for Barney . Barney then shows up claiming the hand of Emma.
He is then proclaimed king. Emma says to him:
Quote:
“There is no other way, my lord King,” she said with grave dignity. “With her blood your mother requeated you a duty which you may not shirk. It is not for you or me to choose. God chose for you when you were born.”
Unquote.
Thus with the line: God chose for out ERB unites the stories of Little Lord Fauntleroy and The Prince And The Pauper. The Little Prince of ERB’s early years returns to his God appointed place. He and Emma are united.
One believes that the story and its ending was intended for Emma to observe ahd heed. Apparently she didn’t because in the next Tarzan story, Jewels Of Opar of 1915, Tarzan and La flirt again.
Anyway The Mad King sequel rounds out the stories of 1913 bringing Burroughs’ springtime to an end. The tragedy is that Emma couldn’t foresee that ERB had tapped into the Mother Lode. No matter how improvident ERB would continute to be the money would always be there to continue their new life style. Perhaps if she had surrendered to fate and Made ERB her king in fact both she and La would have been united in one figure.
It seems that the Cave Girl, The Eternal Lover and The Mad King explored ERB’s relationship with Emma fromt he beginning to the point aht ERB was minded to replace her with an ideal woman.
The notion would develop in his mind until in 1927 he actually did so.
The three sequels ended the quest of his Springtime. His youthful enthusiasm was exhausted. From this point on he would compose more formal novels searching for story lines.
Personally I find his post 1914 to 1920 work some of his best. The two sequels to The Mucker yet to come are outstanding.
Female problems continued to dominate his work. Then in 1921 he read a work on male-female relations by E.M. Hull that had a profound effect on him. that was the novel of The Sheik. I would like to do a review of that next before I return to the Tarzan series.
Pt. VI Springtime For Edgar Rice Burroughs
August 15, 2007
Springtime For Edgar Rice Burroughs
Part VI
Working Around The Blues
by
R.E. Prindle
Nineteen-fourteen dawned with ERB trying to work around his problems. As unbelievable as it may seem he wrote three stories in the first quarter of that year- The Beasts Of Tarzan, The Lad And The Lion and The Girl From Farris’s.
Beasts probably relates to his continuing problems with Emma. Quite probably the wishes expressed in Nu Of The Niocene remained unfulfilled as Tarzan and Jane or ERB and Emma become estranged or separated in Beasts. The separation is reminiscent of the separation in Tarzan The Untamed, Tarzan The Terrible and Tarzan And The Golden Lion. Obviously something is going on in the marriage but apart from inferences in the novel we can’t be clear as to what. Suffice it to say the couple remains together.
Then in February ERB began what must have been a painful book for him to write. He began the book on 2/12/14 almost exactly one year after his father died. George T. passed away on 2/15/13. ERB had had a year to mull over his dad’s dieing and Lad is the result.
George T. appears to have been a difficult father for his sons, all of them not just ERB. Except for ERB slipping the noose by becoming a writer none of the Burroughs Boys would have been a success in life by business standards.
The hangman’s noose is a minor theme in the stories of the teens appearing most significantly in Bridge And The Oskaloosa Kid. The noose also make an appearance on the 100th anniversary of George T.’s birth in 1933’s Tarzan And The Lion Man. While the noose was intended for Burroughs alter egos in the teens in Lion Man the situation is reversed when Tarzan/ERB places a noose around the neck of God/George T. Perhaps the strange piebald appearance of God reflects ERB’s love/hate relationship with his father.
Little study of George T. Burroughs has been done. But if we postulate the burning of his distillery as the central fact of his later life from which he never recovered but edged slowly downhill then the burning of God’s castle may possibly represent the burning of the distillery.
It is possible that the fire changed the personality of George T. He may have been one man before the fire and another after. It is significant that God/George T. is associated with cannibalism. Thus the theme of cannibalism that looms large in the corpus may be associated with ERB’s relationship with his father. Thus the noose and cannibalism would be symbols of ERB’s treatment by his father.
In Lad his father surrogate is a deaf mute crazy old coot who torments the Lad and his Anima every day of their lives. I am not clear on ERB’s relationship with his mother but let us compare a passage from Howard Pyle’s story of King Arther from Volume II The Story Of The Champions Of The Round Table which it is very probable Burroughs read and was influenced by:
Quote:
So she (Percival’s mother) kept Percival always with her and in ignorance of all that concerned the world of knighthood. And though Percival waxed great of body and was beautiful and noble of countenance yet he dwelt there among those mountains knowing no more of the world that lay beyond that place in which he dwelt and the outer world, then would a little innocent child. Nor did he ever see anyone from the outside world, saving only an old man who was a deaf mute.
Unquote.
Transfer the above setting to the deck of the derelict, make the old deaf mute vicious and mean and possible substitute the lion for the mother and you have transposed Percival to the Lad And The Lion.
We don’t have enough information to be certain of the characters of George T. and Mary Evaline. ERB is reticent about his mother. Either I’m missing the key or she doesn’t appear in the stories. Not much has been said of her after her husband’s death in 1913 and her own death in April of 1920 while visiting in Tarzana. Prior to that she had been visiting her sons spending three months at a time with them. Whether she had just began this rotation is uncertain but this was the first time she had visited ERB and Emma.
George T. figures more largely in Burroughs’ writing while always in a love/hate relationship. I never had a father so I have that blind spot in my education meaning that, perhaps, I may not be the best judge of the father-son relationship. My evaluation of George T. is that he wished to maintain a dominant role over his sons. Perhaps, like many fathers, he was fearful that as his powers waned theirs would wax and they would become more powerful than he. Something along the lines of the Greek god Cronus who, having been warned that one of his offspring would replace him swallowed them whole as they were born. A stone was offered Cronus in place of his youngest son, Zeus, who did grow up to replace him.
It is interesting that George T.’s youngest son, ERB, was able to escape his meshes just as the father died.
The letters of the Burroughs Boys – George and Harry- from Yale indicate that while their father supported them he kept them on a short leash. It is true that they began college after the distillery fire so that he may have been more liberally handed before the fire so as to bind the Boys to him but we won’t know.
Having finished Yale as graduates of the Sheffield Scientific School they returned home to take up roles in the battery business that succeeded the distillery. They were only able to escape their father’s domination when Harry became ill from battery fumes requiring his living in the dry climate of the West. George begged to follow him and was so allowed.
George T. didn’t own the battery business outright in its first years. It would be nice to know something about his business associates in that business.
I have already detailed the difficulties he placed in ERB’s life that were detrimental to the formation of the lad’s character.
And then we have Herb Weston’s characterization of George T. as a stern man of the old school who he yes, sirred and no, sirred and got along with him famously.
It is not impossible that John Carter is the idealized character of ERB’s father. Carter’s own role in the Mars series does not disappear after 1913’s Warlord Of Mars but his role is greatly curtailed. A possibility.
I think it is a near certainty that the deaf mute old coot of the derelict is the negative father. In Lad he doesn’t die naturally but is killed by the Lion who rips his face off. This must be an affect of his father’s death as after the Lion kills him the Lad and the Lion continue to drift along for several months before the ship gently beaches itself, the tide goes out and the two walk ashore. Then, just as Percival saw the knights, being drawn into the outside world, the Lad sees the Arab ‘knights’ being also drawn into the outside world. He experiments with the burnoose just as Percival experimented with the armor.
Thus a year after his father’s death Burroughs attempts to escape from the ‘crazy old coots’ shadow.
That done, ERB then turns to a story begun the previous May to finish it. The long period of incubation indicates the difficulty he had in getting the story out. The Girl From Farris’s tells of the period from his bashing in 1899 to his return from Idaho in 1904.
It is a difficult story vis-a-vis Emma. ERB places his heroine in a brothel in Chicago. Harris’s, the original location, was actually a famous brothel; Harris himself being a noteworthy figure which is probably why the name was changed to Farris’s.
The woman escapes from the brothel. After a series of adventures in Chicago she leaves for Idaho where she meets the hero Ogden Secor again who had aided her back home.
Secor is in a desperate psychological state and that is probably an accurate description of ERB’s state of mind during those few years.
The woman is identified and taken back to Chicago where after a bit of legal hoopla she is exonerated, we learn that she was never a prostitute and she and Secor are married. After this number of terrible years something good happens to Secor and, one assumes Burroughs, the ray of light breaking through the clouds.
At this point in March, nearly April, of 1914 ERB and the family return to Chicago, after once again auctioning off their belongings as they had done in Salt Lake City before returning to Chicago in 1904. This has to signify in Burroughs’ mind that he had reversed his shameful performance of ten years earlier. He undoubtedly expected Emma to also accept 1913-14 as a redemption of 1903-04. Just as he had gambled and lost in ’03, in 1913-14 he had gambled and won.
Even though according to him he was living hand to mouth he ordered a new automobile (not a used Velie) for delivery upon his arrival back in Chicago. If the car was Burroughs’ Hudson then that would indicate that he had visited Baum in Hollywood as Baum drove a Hudson. ERB would want to emulate his hero. Then within a month or two the Burroughs left their old address in Chicago to move into the fancier suberb of Oak Park. Perhaps this move was made possible by the expected book royalties. Thus Burroughs continued to spend in anticipation of income rather than from money in his pocket. So Burroughs kept his hopes and dreams alive.
The springtime of ERB thus ended. The incredible psychological release of success was now to be tempered by new realities. The act of writing would now become a full time job. From 1911 to 1913 he wrote from hopes and dreams. Now he would have to settle down to turning out two or three books a year for magazine sales plus book royalties and newspaper royalties soon to be joined by movie revenues. ERB had won the gamble of quitting his day job. The Roving Gambler could now turn to the pleasures of life on the yacht.
But first there was the unfinished business of the three stories- The Mad King, The Cave Girl and The Eternal Lover- to be taken care of.
Properly belonging to 1913 the three sequels would take up a large block of time in 1914 which makes that year a transition year.
I will review the stories in the sequence in which they were written: The Cave Man July-August of 1914, The Eternal Lover, August and September and The Mad King, September-October.
Next:
Part VII
The Denouements.
Part 4c Springtime For Edgar Rice Burroughs
July 10, 2007
Springtime For Edgar Rice Burroughs
by
R.E. Prindle
4c
How Waldo Became A Man
In the complex of meanings of Waldo the question is how much Burroughs bases the character on himself. In the question of health there is no question that Burroughs had issues after his bashing in Toronto in 1899.
Judging from the Girl From Farris’s his health was a serious problem for him at least until early 1914 when he finished Farris’s. During those years he suffered from debilitating excruciatingly painful headaches for at least half the day. He either awakened with them or they developed mid-day. There is evidence that he became interested in Bernarr Macfadden’s body building and health techniques when Macfadden opened his Chicago facilities in 1908. If he were involved then perhaps the benefits of such a regimen were becoming apparent in1913-14. In 1916 in the photograph in puttees taken at Coldwater he looks like a healthy specimen and proud of it.
ERB gives Waldo the wasting disease Tuberculosis putting him on a regimen of exercise in the healthy dry air of his island thus curing him within a few months. This process is reminiscent of Grey’s hero John Hare of Heritage Of The Desert or the development of the Virginian in Owen Wister’s novel.
Burroughs claimed that his writing was heavily influenced by his dreamworld. If so then in this story as well as his others each character must represent a real person who figures in his life; the story must represent a real situation in symbolical form.
As authors so often claim their characters are composites it is likely that Burroughs also combines memories of other people with his own dreams. As Burroughs consciously manipulates his dream material he tweaks it into shape to make an entertaining novel then overlaying his conscious desires on his subconscious hopes and fears.
page 1.
In addition Burroughs retains his literary influences using them to give form to his dreamscapes. Indeed, his influences fill his mind so full they become part of his dreamscapes. The island he creates is similar to but not identical with Jules Verne’s Mysterious Island. This becomes very apparent in the sequel, The Cave Man, when Waldo sets about to improve his little society. He isn’t as obsessive-compulsive as Verne but along those lines.
Verne’s island figures prominently in many of Burroughs narratives. Oddly the book isn’t in his library.
ERB began telling his life’s story the moment he took up his pen. While John Carter seems to be dissociated from his own personality Tarzan is a true alter ego, a psychic doppelganger. Tarzan Of The Apes is a symbolical telling of his life’s story from birth to 1896 while the Return of Tarzan covers the four years from 1896 to 1900 and his marriage. (See my Four Crucial Years In The Life Of Edgar Rice Burroughs here on ERBzine.)
The Girl From Farris’s deals with the troubled years from 1899 to, it appears, March of 1914. Thus Cave Girl addresses his difficulties in making the transition to writer and then full time writer with the attendant marital or sexual problems. These marital or sexual problems occupy him through many novels in this first burst of creativity from 1913 to 1915.
Porges in working from Burroughs’ own papers in his biography has very little input from outside sources but some. The first material we have to work with from an outsider’s point of view is Matt Cohen’s fine edition of Brother Men, the collection of the Burroughs-Weston correspondence. Weston being ERB’s friend from MMA days. At the time of the divorce they had been in touch for forty years.
However I think that figure may be a little misleading as the two men had very little contact during that period. ERB met Weston in 1895 at the MMA at the beginning of the school year. He was one year younger than ERB. As Burroughs left the MMA in May of ’96 the two must have become fast friends in just eight or nine months. It isn’t probable that they met again before 1905 when Weston was passing through Chicago with his wife Margaret. At that time both Westons would have met Emma. From that time to the end of ERB’s Chicago period except for the occasional brief layover in Chicago the relationship was carried on by correspondence although as Burroughs seems to have some knowledge of Weston’s home town, Beatrice, Nebraska as evidenced in the second half of The Mad King it is possible he and Emma visited Weston but that would have had to have been between March ’14 and August ’14. Narrow window.
Thus when Weston talks so knowingly of Burroughs’ character in the letter of 1934 I will refer to I would have to question the depth of his knowledge. At any rate he claims to have knowledge of the difficulties of the marriage.
Weston was completely devastated by the announcement of the divorce. He immediatly sided with Emma breaking off relations with ERB for several years.
It appears from the letter of 1934 reproduced on page 233 of Brother Men that he contacted Burroughs’ LA friend Charles Rosenberger for information on the divorce. We have only Weston’s reply but not Rosenberger’s letter.
In reply to Rosenberger Weston says:
Quote:
I have known Ed since the fall of ’95. He has always been unusual and erratic. I have told Margaret many times, when Ed has done or said anything which seemed sort of queer that as long as I had known him he had always done or said such things.
(One of the most significant odd things would have been Burroughs leaving the MMA in mid-term in May to join the Army. One imagines that when he didn’t show up for classes next day the faculty asked: Where’s Burroughs. Perhaps Weston was the only one who knew and had to say: Uh, he joined the Army.)
I suppose looking back, that the fact that Ed has always been unusual, erratic and perhaps queer, has been his great charm and attraction for me.
Unquote.
I don’t know about you but if my best friend talked about me like that I would be less than flattered. There is another back handed compliment that Weston made to Burroughs’ father in his defense.
Burroughs’ father had made the comment to Weston that his son was no damn good. Good to have your dad on your side too. Weston defended ERB vigorously saying that he thought there was plenty of good in ERB, he just hadn’t shown it yet. Thank you, Herb Weston.
If one judges from the actions of Ogden Secor in Girl From Farris’s after he was hit on the head and if his actions approximated those of Burroughs from 1899 on then there was probably a very good reason for ERB’s unusual, erratic perhaps queer behavior apart from the fact that ERB had developed the typical character of his difficult childhood.
In reading the correspondence Weston comes across as a very conventional and highly respectable person; in other words, stodgy. It must have been that settled bourgeois quality in him that ERB appreciated. Weston did many of the things that Burroughs would have liked to have done. Weston did go on to Yale from the MMA which is what Burroughs would have liked to have done. Weston did become an officer in the Army.
On page 157 of Brother Men is a discussion of the Spanish American War. If I read it correctly Weston actually served in Cuba with a Tennessee regiment. So Burroughs had reason to be envious of him as he failed in his own attempts to get into Teddy Roosevelt’s Rough Riders.
Nevertheless Weston’s evaluation of Burroughs uses some strong language who after all didn’t have that intimate a relationship with him: unusual, erratic perhaps queer. Honestly, I don’t think I would have a friend very long who thought of me that way.
Weston is bitterly disappointed but later in the letter he refers to Burroughs as a crazy old man so, at the least, we can assume that to the average mentality Burroughs appeared eccentric. As one in the same boat I can’t help but root for the author of Tarzan. What but an unconventional mind could have conceived such a story.
Burroughs antecedents had created his persona by 1895 so the crack on the head in Toronto merely added to his unusual persona.
Apart from any inferences about Ralph Waldo Emerson and the Transcendentalists the sickly character of Waldo may represent Burroughs’ own health problems from 1899 to the time of The Cave Girl.
I feel certain that Burroughs followed some sort of health or body building regimen from perhaps 1908-09 when the American body building king Bernarr Macfadden opened his Chicago facilities to 1913. Although Ogden Secor of Girl From Farris’s was still sickly in 1914 perhaps Burroughs health was improving as Waldo evolves from a skinny sickly person to a ‘blond giant’ before our eyes. ‘Blond Giant’ also brings to mind Nietzsche’s ‘Great Blond Beast.’ I think it would be pushing it to say Burroughs read Nietzsche, nevertheless Burroughs always seems to be well informed when you look closely. He might easily have picked up references to the ‘Blond Beast’ from newspapers, magazines and conversation.
Weston is especially incensed at Burroughs leaving Emma who both he and his wife Margaret seem to have preferred. They did travel to California to visit Emma while ignoring ERB.
Weston quotes Rosenberger to the effect that ERB told Rosenberger that he had always wanted to rid himself of Emma. To which Weston replies:
Quote:
Charming, unusual, erratic personality that Ed is, there is no woman on earth that would have lived with him, and put up with him except Emma, and do not be fooled! Emma suited Ed plenty, until this insane streak hit him.
Unquote.
So we have an outsider’s view of the situation. He considers Burroughs over the line in his personality to be redeemed by his charm. Weston had asked Rosenberger his opinion of the situation between ERB and Emma. ERB had apparently told Rosenberger after the split that he had always wanted to rid himself of Emma.
As far as Burroughs’ persdonality goes it would be in keeping with a person of his background who had been bounced from school to school. Waldo may in part be a nasty caricature of the East Coasters Burroughs associated with at the Phillips Academy. As is well known Easterners at the time and still today disdain those from the West. One has the feeling that Burroughs valued his Idaho experiences highly thus the transformation from the wimpy Easterner of Waldo to the Blond Giant of the great outdoors may be Burroughs snub of his Eastern classmates.
At any rate when Weston met Burroughs at the beginning of classes in ’95 ERB’s personality seems set.
By ‘saying things’ one presumes that Weston means Burroughs had an outsider’s ‘eccentric’ sense of humor. I have a feeling that a few of we Bibliophiles know where that’s at. Certainly Burroughs’ stories reflect this trait. So, between Burroughs and Weston we have a clash of two different backgrounds.
As to Emma I believe that Burroughs was always dissatisfied with the fact that he had married when he did whoever he might have married. He has been quoted as saying that Tarzan never should have married so that idea can probably be applied to him.
If circumstances hadn’t forced his hand he very likely would have remained single. According to his psychology the right time for him to find a woman and marry would have been after 1913 and his success when he was in effect born again and a new man.
So when he says he never really wanted Emma as a wife I’m sure that is true. However he did marry the woman. So from 1913 to 1920 we have Burroughs struggling with his desire to honor his life long committment to Emma and his contrary desire to find his ideal ‘mate’ a la Dejah Thoris, La, Nadara and a number of others. Not so easily done in real life and after great success but still possible.
Added to his problem was his embarrassing behavior in Idaho when he gambled away the couple’s last forty dollars. Emma reacted badly to the Western interlude in their marriage. Burroughs’ rather feckless attitude toward earning a living between the return from Idaho and his early success in 1913 undoubtedly caused emotional problems for Emma but as Weston says she stuck by him during those lean years and as he says, there were a lot of them.
Even in 1913 when the couple earned the first real money they had ever seen Burroughs was recklessly spending it before he got it based only on his confidence that he would always be a successful writer something which by no means necessarily follows.
Emma was very proud of Burroughs as the photo ERBzine published of the couple in San Diego shows however her pride obviusly conflicted with her fears so that she may have nagged ERB in what he considered an unjustified way.
On one level Cave Girl can be construed to be a record of their relationship up to the moment with Burroughs trying to reconcile the relationship according to his confident understanding of the situation.
Writing in February-March in Chicago we have this view. In September of 1913 the family left for San Diego. Writing in San Diego during October-November in the Mad King things seem to be deteriorating as Burroughs seems to be pleading with Emma to be reasonable. Thus the Mad King concerns Prince and Pauper doppelgangers who are appealing to the same woman.
This situation may have been caused by a situation that would be very reminiscent to Emma of her situation in Idaho of ten years earlier. On this trip in which ERB and Emma were as alone and isolated as in Idaho ERB was taking another very large gamble with Emma’s and her three little children’s wellbeing at stake. As ERB proudly tells it the family, no longer just a wife, but a family of five were within an ace of being flat broke if any one of the stories Burroughs wrote in 1913 failed to sell. Unlike Idaho this was a gamble the Roving Gambler won. Now, perhaps Burroughs thought this redeemed his earlier faux pas, probably to himself it did. But what about Emma? What terrific anxieties assailed her as she wondered whether they would have a roof over their heads from day to day.
We need more facts. Perhaps the move from Coronado to San Diego was forced by necessity to reduce costs. Perhaps selling the Vellie was necessary to raise cash. Thus Emma in the midst of this actual plenty of a $10,000 income was a virtual pauper in silks and diamonds. Would there be any wonder if she were cross and nagging? As Weston said there were difficulties in living with Burroughs.
Burroughs then rather than attempting to make reasonable adjustments in his behavior yearned for the perfect mate who would ‘understand’ him.
Nevertheless he had to bear the burden assigned him. Let us assume that as Weston said, at one time Emma suited Ed plenty. That’s an outsider’s opinion but the evidence of this group of novels is that ERB was doing his best to rectify his past for Emma. If Waldo is portrayed as clownish I’m sure that ERB had played the clown in real life for some time. As Weston said ERB had always said and done unusual things. He doesn’t say what they were but in all likelihood the things he said and did were meant to be jokes, to be funny. After all he describes Tarzan as a jungle joker. The jokes that Tarzan perpetrated originated in ERB’s mind so he had to think those jokes were funny. They were usually practical jokes. No one really like a practical joker. The psychological needs that go into a practical joke are compensatory.
Where he failed Emma in the past he seems to be trying to make up for it. Perhaps his financial gamble in 1913 in some way compensates for his gambling failure in 1903 reversing the outcome of 1903 and making it alright. His actions in 1913 are so zany one has to ask what he thinks he is doing.
e.
Leaving their little Eden Waldo and Nadara set out for her village where Korth and Flatfoot await him with Nagoola in the background.
Thus Waldo’s tasks as set for him by Nadara are to kill Korth and Flatfoot. Waldo quite correctly realizes that these two tasks are beyond his present powers. So, within sight of the village he makes excuses to Nadara then abandons her running away. He heads out to the Wasteland. He appears to be living in a near desert.
Over the next several months he transforms himself from a tubercular wimp into a ‘Blond Giant.’ Tarzan has black hair so perhaps Waldo has to be blond.
One can’t be sure but this period may represent the years from John The Bully to ERB’s proposal to Emma. At any rate Waldo can’t forget Nadara having a longing for her. During his period in the Wasteland he fashions weapons for himself that make him superior in prowess to the cave men. He fashions a spear, a shield and what Burroughs jokingly, I hope, refers to as a sword, that is a sharp pointed short stick with a handle. No bow and arrow. So rather than a primitive Tarzan we have a primitive Lancelot. Waldo is actually outfitted as a knight, a la Pyle, while when he acquires the pelt of Nagoola he will be, as it were, encased in armor. So Pyle, or at least Arthur, is an influence.
In a comedy of errors Nagoola manages to kill himself by falling on Waldo’s spear. In one sense this means that Waldo has invested his sexual desires in Nadara while perhaps it is symbolic of Burroughs’ desire to do the same with Emma. At the same time the panther skin makes Nadara the best dressed girl around. It is perhaps significant that he kills Nagoola first before Korth and Flatfoot.
If one looks again at that ERBzine photo of ERB and Emma in San Diego one will notice that Emma is wearing some spiffy new togs. In her father’s house Emma was a clothes horse. In another ERBzine photo showing ERB and Emma walking in the wilds of Idaho Emma is still dressed to the nines while ERB shambles along beside her in a cheap baggy suit.
From that point in 1903 to the efflorescence of wealth in 1913 Emma had to make do with whatever garb she could afford which must have been depressing for her. As Weston says that was a sacrifice she was willing to make for her man.
Not in 1913 in Cave Girl but in 1914 in Cave Man Waldo invests Nadara with Nagoola’s pelt. Now, Waldo suffered grievously to acquire this skin. That was a major battle out there in the Wasteland. Let us assume that the skin represents Waldo’s sexual desires and that in clothing Nadara in the skin he is making her his queen or princess.
Thus in 1913-14 for the first time in his life ERB is able to reestablish Emma as a clothes horse. He has finally been able to do his duty as a man and husband. She can now buy as many clothes of whatever quality she likes and ERB is happy to have her do it. So, in a symbolic way ERB had a terrific struggle that scarred him psychologically as Waldo was physically scarred by the talons of Nagoola. Now, Burroughs was proud to be able to dress Emma to her desires. In the same way that the panther represents Waldo’s investing Nadara with his sexual desires so Emma’s clothes represent the same to ERB.
It was now up to Emma to forgive ERB for his failings and treat him as her hero. Perhaps ERB was a little premature. I think that he would have had to woo her all over again. While he had conficence he would be able to go on writing indefinitely the surety of such was problematic to others like Emma and actually ERB’s editor at Munsey, Bob Davis. Davis told him point blank that guys like Burroughs start strong, shoot their wad and fall out after two or three years. As far as others were concerned Burrroughs future remained to be seen. The evidence is that Davis and other editors thought that Burroughs had Tarzan and that was it. Apart from the Mars series how much of this other stuff was pubished to humor Burroughs to cajole more Tarzan novels is a question. Still, the fans seemed to receive it well. Cave Girl was even serialized in the New York papers.
Nadara has set Waldo three tasks all of them murderous. He is to kill Nagoola, Korth and Flatfoot. Having fulfilled the killing of Nagoola Waldo after several months sets out to return to Nadara to fulfill his last two committments.
Before he invests Nadara with Nagoola’s pelt he first kills Korth and Flatfoot. These are monster battles where like the knights of old, Lancelot, Waldo is hurt near to death.
Now, what would Emma nag ERB about during those lean years? The clothes have already been discussed so that leaves the monetary success to acquire them. So the slaying of the pair of cave men may represent financial success. Financial success came with the creation of John Carter and Tarzan. So let’s assume that Korth represents John Carter and Flatfoot Tarzan. The creation of the two or the slaying of those dragons opens the way for the hero Waldo/ERB to present Nadara/Emma with the first task, clothing.
Having killed Korth and Flatfoot Waldo still has to make up with Nadara for abandoning her at the threshhold to her village. Not an easy task. Waldo pleads that he has done everything she asked but she remains obdurate. This probably relflects ERB and Emma’s situation. A situation that apparently was never satisfactorily resolved.
But then it seems as though there is a change in the characterization and Nadara reverts back to Nadara of the beginning of the book while Waldo, believe it or not, becomes a god, if Nadara had known what gods were. Waldo scrambles up some fruit trees to toss down some food that seems to bring them together. In the last pages Burroughs gets schmaltzy writing close to purple passages.
At this time Nadara spots a yacht out over the waves. The yacht is a major theme during the teens and especially in this 1913-14 period. The significance seems to be that Burroughs envisioned his early life as The Little Prince as life on a yacht. Then the big storm comes changing his life as it sinks. Then begins the struggle for existence capped by the eventual triumph.
The yacht first appeared in Return Of Tarzan. This is its second appearance. Tarzan wasn’t on the yacht in Return and Waldo doesn’t get on the yacht in Cave Girl although he does in the sequel The Cave Man but that was a year later in 1914. So things are evolving rapidly in ERB’s psychology.
In this case he plans to join the yacht that he recognizes as his father’s. Having abandoned Nadara once she imagines he is about to do so again so she runs off.
Thoughts run through Waldo’s mind as he envisions a return to civilization with Nadara.
Quote:
For a time the man stood staring at the dainty yacht and far beyond it the civilization which it represented, and he saw there suave men and sneering women, and among them was a slender brown beauty who shrank from the cruel glances of the women- and Waldo writhed at this and at the greedy eyes of the suave men as they appraised the girl and he, too, was afraid.
—-
“Come,” he said, taking Nadara by the hand, “let us hurry back into the hills before they discover us.”
Unquote.
And so Waldo decides to remain in the stone age.
He and Nadara had left the little bag containing the relics of her mother behind. The crew of the yacht discover the bag just on the inland side of the forest.
Then we discover that Nadara is in fact the daughter of French nobles. Burroughs seems to have some love affair going on with the French. Many of his most attractive characters such as Paul D’Arnot, Nadara here, Miriam of Son of Tarzan are Gallic. So Burroughs admires most the English, the French and the Virginians it would seem.
Nadara is the daughter of Eugenie Marie Celeste de la Valois so she is a legitimate princess.
Thus ends the Cave girl with seeming finality. The way is open to the sequel but the closing seems final.
I haven’t read a book that replicates the final scene but I suspect that ERB borrowed it. I wouldn’t be surprised to learn of an earlier duplicate.
End Of Part 4c.
Part 4a,b Springtime For Edgar Rice Burroughs
June 21, 2007
Springtime For Edgar Rice Burroughs
3.
In The Beginning:
The Renascent Burroughs
a.
The psychological release Burroughs experienced when he began to realize the potential he had always felt must have been especially gratifying. In all likelihood he believed he was beginning a new life, born again, as it were. It wouldn’t have been unusual in this circumstance that he wished to dissociate himself from his entire past of failure.
For this reason it is possible that California loomed as the destination in which his new life would unfold. Making the change was difficult and would take him six years to consummate. One asks, why California? Why not Florida, for instance. I think the answer may be in his three most favorite novels: Mark Twain’s Prince And The Pauper, Little Lord Fauntleroy and Owen Wister’s The Virginian. Wister posits the West as a place of redemption and fulfillment while Burroughs youthful visit to Idaho may have had that effect on him. Hence Waldo the consumptive lands on an island as primitive as Idaho was to Chicago and becomes a man. So Burroughs may have viewed his visits in the West.
In the Prince And The Pauper a Prince becomes a Pauper and a Pauper becomes a Prince. In Fauntleroy the unknown princeling discovered his true identity thus exchanging the role of Pauper for a Prince while his alter ego the pauper Dick The Shoeshine Boy is transformed as well and through luck and pluck assumes a role of success in California as a rancher at the end of the story.
The Burroughs born a princeling then disinherited to a Pauper reassumed his role as a Prince but he had been inefaceably declassed hence though now a Prince as Fauntleroy he retains the psychology of the declasse as in the character of Dick The Shoeshine Boy. Dick at the end of Fautleroy moves to California where he finds work on a rach eventually becoming a success as a rancher himself.
It seem obvious that burroughs considered Little Lord Fauntleroy a book of destiny. Thus California would appear as his destiny. I believe that the reason for the six year delay in the actual move was necessitated by a need to combine the Fauntleroy and Dick the Shoe Shine Boy or The Prince and the Pauper into one identity. He had to have enough money to support the appearance of the Prince. I haven’t figured out why he wanted to raise hogs as yet but when he moved he anticipated only buying 20-40 acres which was well within his means, but when he arrived there Colonel Otis’ magnificent estate presented an opportunity to realize both identities in a property he couldn’t resist although he may have known he was acting in an unwise manner.
Even then it may have been possible to sustain the property if his economic situation hadn’t come under attack by the Judaeo/Red/Liberal Coalition in the early twenties.
A second very major p;roblem for him was Emma who now definitely became unwanted baggage. But, he also had the three children who were also as definitely wanted baggage. It is possible that for their sake he didn’t abandon Emma until they were grown.
His Anima ideal was foreshadowed in Dejah Thoris while in Tarzan Of The Apes he creates the stodgy but beautiful Jane Porter as a flesh and blood woman but not an Anima ideal.
The actual split begins to occur in The Return Of Tarzan when Burroughs bursting with confidence realizes that he is about to realize his visions of self-worth. At that point the past and all related to it becomes hateful to him. As might be expected he wanted to put all that behind him. Thus in creating a land of his fossilized past in Opar he also creates a vision of the ideal woman he would like to have in La of Opar. In Return the conflict between Jane and La becomes apparent when La is about to sacrifice Jane on the altar of the Flaming God. That she doesn’t means that Burroughs has elected to stay with Emma undoubtedly for the children’s sake.
But he begins to toy with ideal images in resolution of his sexual dilemma. Another woman becomes a possiblity that didn’t exist before. It would seem apparent that as Burroughs fame grew and he became a desirable sex object to women that opportunities for philandering would present themselves. At one time I believed for certain that he didn’t. Now I am less certain but there is nothing to indicate he did.
Nevertheless he does begin to explore other ideal possibilities. Nadara of Cave Girl can be seen as one of those explorations. Having created other possibilities in La of Opar Burroughs begins to develop the idea with the cave girl, Nadara. She is perhaps the most human of all of Burroughs’ Anima ideals. She is the daughter of civilized French aristocrats raised by a caveman to be a primitive woman. Thus she has none of the civilized inhibitions especially toward sex. Burroughs will now begin a series of novels concerning the sexual relationship well in advance of what he may have heard about Freud.
Once Nadara has accepted Waldo as her mate she is ready to cohabit. Burroughs seems to be advocating this as a sociological ideal; a revolt against the strict limits of civilization. However in a clash of cultures Waldo who is subject to the strict limits of civilization finds it impossible to establish sexual relations unless they have married according to civilized rites and customs. As there is no one in this stone age society to perform these rites Waldo keeps putting consummation off until such an opportunity arises, if it ever shall.
Bearing the psycho-sexual situation in mind an interpretation of The Cave Girl is possible on a number of levels. The story is set in motion with a variation of what will become the familiar ship wreck motif. In this case the Prince, Waldo, is washed off the deck of the ship by a huge wave that deposits him on the strand of a large stone age island in the South Seas. Thus Waldo has to begin life without any survival skills, born again as it were as a new born babe. He has become the Pauper.
At this point it might be best to introduce the major sources for the story that I have found. As usual there are several.
And then I received an email a day or so before this writing from Mr. Caz Cazedessus of Pulpdom Magazine. Having read the first couple sections he pointed out that Mr. J.G. Huckenpohler had written an article in the first Pulpdom issue relating Cave Girl to Zane Grey’s Heritage Of The Desert. I haven’t read Huck’s essay but I have read The Heritage Of The Desert which I have just reviewed. I can see a possible line of argument that shows a number of similarities in the plotting of the two novels.
Heritage was published at some point in 1910 while Cave Girl was written in February-March of 1913. That does leave a sufficient window for Burroughs to have read Grey’s book but it seems a little light especially as Grey was a newish author at the time without a definite reputation. However whether or not he may have read the book earlier it is possible that he read the book shortly before writing Cave Girl having elements of his plot suggested to him.
Thus both Waldo and John Hale, the hero of Heritage, are consumptives or ‘lungers’ as they say Out West. Waldo is from Boston, Hare from Connecticut. Hare goes West to Mormon Country to begin his regeneration while Waldo lands on his island. In both cases a woman is involved and two enemies are overcome by their respective heroes. So, as I say, I don’t know Huck’s argument but I’m sure it’s a good one. There are good reasons to believe that the plot line was an influence, an additional influence, on Cave Girl. Thus Heritage would be another influence on Cave Girl. OK, Caz?
As Burroughs was beginning life over there is also a definite influence from the first eleven chapters of Genesis from the Bible which I will make apparent in my essay.
Another very major influence seems to be the King Arthur mythology. I will make this apparent as I go along. While there is no doubt that Burroughs would have been familiar with Genesis it might do to try the root out his possible Arthurian influences.
While we have at least a portion of Burroughs’ library listed here on ERBzine we should never gorget that while growing up ERB would have had access to the libraries of his brothers as well as that of his father. George T.’s library would have gone back to the 1840s and probably earlier not including the then English classics such as Milton’s Paradise Lost, Bunyan’s Pilgrim’s Progress et al.
One imagines that there were Arthurian titles in the collections, at least Mallory’s Arthur. If the young Burroughs didn’t read the volumes through he would at least have handled them, browsed them and looked at the pictures, if any. We know his brothers recommended the related Greek mythology to him.
Certainly the medieval world was more often discussed in papers and magazines then than in our day. And then Burroughs did like Tennyson having his collected poems in his library. Thus ERB was likely familiar with the poet’s Idyls Of The King dealing with Arthurian stories. And those not following Mallory. Perhaps the most important Arthurian influence was Howard Pyle’s four volume retelling that while similar to Mallory’s differs significantly while Pyle adjusts the story to his own perceptions and moral concepts.
The reputation of Pyle would have loomed large to ERB. There is one Pyle title in his library, Stolen Treasure, but Pyle’s reputation as an illustrator would have drawn ERB’s attention to him. Pyle was the most influential illustrator of his time and perhaps in US history. His disciples were legion including Burroughs’ own illustrator, St. John. Pyle founded what is known as the Brandywine school of illustration.
It should be borne in mind that Burroughs had an aborted career as an illustrator before he began his successful career as writer. Burroughs was very proud of the time he spent at the Chicago Art Institute. So it would seem that ERB would have kept up on Pyle, Maxfield Parrish and others.
Pyle began rewriting the Arthurian story in 1903 completing the last volume in 1910 so Burroughs had plenty of time to ingest and digest the work before he began to egest it. Nor would Pyle and Tennyson be his only Arthurian influences.
I didn’t catch this in time to include the idea in my review of The Lad And The Lion but that story seems to be highly influenced by Pyle’s telling of the story of Percival from Pyle’s second volume, The Champions Of The Round Table. Naturally Burroughs borrows elements rather than the complete story.
Percival, I follow Pyle, was an orphan living in the forest with his mother far from the haunts of men. P. 263, prologue to Percival.
Quote:
Nor did he ever see anyone from the outside world, saving only an old man who was a deaf mute.
Unquote.
So Burroughs took the hint of the deaf mute and elaborated the idea.
The Lad’s entry into the world follows that of Percival. So also the Lad’s first sight of the desert horsemen replicates Percival’s first view of the ‘angelic’ knights.
As I did mention in my review there is a similarity between lad’s being named Aziz, translated as Beloved, by Nakhla and Percival’s thinking his name was ‘Darling Boy’ as his mother referred to him. If this last connection is valid then Burroughs also read some other Arthurian story as Pyle doesn’t tell his version in that way.
So, as usual, Burroughs mines the literature of the world to tell his story. Just as I was not aware of the influence of Grey’s Heritage Of The Desert I’m sure there are more I haven’t noticed. I may even find more as my essay unfolds.
Across the strand at no great distance is a forest representing the search for self-discovery and realization. On the mragin of the forest at dusk a figure appears. As we will learn this is the beautiful Nadara but Waldo in his hyper-fear and cowardice imagines the form to be some kind of monster of which he is terrified. The monster stands between him and the food and water he needs. In a metaphoric way then he is between the devil and the deep blue sea. He cannot go back and he is afraid to go forward.
In Burroughs own situation as he is making the fateful decision to quit his day job to devote his life to full time writing the meaning of the metaphor is quite clear.
There is also a way of looking at the tale as retelling of the Biblical Genesis. This opening scene may be represented as the Biblical chaos in which nothing is differentiated with the upper and lower firmaments resting on each other. Then a divine wind arose which separated the upper and lower firmaments.
Waldo is a comic figure while the novel itself is intended to be a comic or satiric novel. Thus Waldo who can stand the tension between the devil and the deep blue sea no more runs howling and screaming into the forest to do or die against the monster.
The shrieking may be seen as a humorous representation of the divine wind. Man having been created first as it seems pursues the phantom who turns out to be a woman. Thus Waldo and Nadara represent Adam and Eve.
Waldo’s charge into the wood can also be seen as a representation of Burroughs’ decision to become a full time writer. This must have been as stressful a decision for him as was Waldo’s charge against the demon. Once through the wood Waldo is presented with a sheer cliff that appears to be inpenetrable. So, another barrier presents itself.
Having traversed the forest that was after all fairly narrow Waldo had seen a woman scrambling up the barrier. Rather than pursue her directly Waldo reenters the wood to pick fruit and refresh himself.
This can be seen as Burroughs’ desperate attempt to become a writer. Another view of the strand and the demon of the forest- between the devil and the deep blue sea- is that Burroughs had to make the desperate attempt to redeem his life by writing. Thus that original difficult decision that might possibly be compared to Waldo’s being washed off deck by the wave while now Burroughs is faced with the even more difficult decision of working at it full time. Thus the charge through the woods might represent his giving up his day job.
It would be interesting to know at what point in the story’s composition his father died. What is even more interesting is that his father’s death did not interrupt his writing schedule. In fact in a year packed with traumatic occurrences nothing did; Burroughs continued to turn out his stories at two month intervals no matter what. It is true that he had several incomplete stories in this year which means he hadn’t thought the stories through so that it is possible that while he averted severe writer’s block when he reached the end of his chain of thought he just stopped, resuming the story when he had thought it out.
A prime example would be The Girl From Farris’s that he began about this time finishing it nearly a year later. The Cave Girl was completed at this point while The Cave Man its other half and sequel was completed the following July and August of 1914. It is possible Burroughs was trying to double his monetary return but I think it more probable that he was writing so fast with such a tight schedule that he didn’t have time to worry over completion so he just terminated his story at a convenient point and moved on to the next one that was also only half thought out.
As all this stuff is based on autobiography I am truly astonished that Burroughs was so undisturbed by the happenings in his life that he had so little reaction. I have read of authors who found writing personal stuff so difficult that they were driven to bed for a week or two at a stretch. I have never faced a long stretch like that but I have sought refuge in bed for a day or two a couple times. So Burroughs writing achievement here over 1913, ’14 and ’15 is fairly remarkable.
At any rate having made the decision to become a full time writer as symbolized by the charge through the wood. Burroughs if faced with an unforeseen barrier so he goes back to pick fruit. This could possibly be seen as having written his intial ideas out, that is John Carter and Tarzan, he had to organize his second crop of stories none of which had the impact of Carter or the Jungle God. Grey’s Heritage may fit in here as Burroughs searching for ideas and plot lines may have the read Grey’s stories at this time or just previously.
Led on by the woman Waldo had mistaken for a demon he now faces the new barrier seeking a way through. He has difficulty finding the path but once on it he discovers the opening through the wall. This is a motif Burroughs will use a number of times most notably in The Land That Time Forgot and Tarzan Triumphant, not to mention the entrance to Opar.
Now, all these openings resemble the birth canal or being born again. In the instance of The Cave Girl the result of the rebirth is self-evident as well as perhaps Tarzan Triumphant when he is about to leave Emma for Florence. The Oparian episodes would have to be examined more closely from that point of view especially as the four episodes occur at critical points in Burroughs’ life while involving sexual conflict between himself and Jane/Emma and another woman represented by his Anima ideal La. Thus, in Golden Lion when Tarzan leaves Opar with La to enter the Valley of Diamonds is it possible that he had a dalliance with another woman? One wonders.
At any rate Waldo squeezed through the opening to come out on a wonderland on the other side. There is never a thought of going back. In fact a cave man places himself between Waldo and the opening driving him forward. This could correspond to the flaming sword protecting the entrance to the Garden of Eden which would continue the biblical motif.
At the same time we have a clear reference to Alice In Wonderland or down the rabbit hole. We know Burroughs was familiar with the two Lewis Carroll stories.
Yet another barrier presents itself. Another cliff is before Waldo this one of cave dwellers another favorite motif of Burroughs especially during this period. Burroughs would have been familiar with actual cliff houses from his sojourn in Arizona with the Army while he would have been fascinated with the replica built for the Columbian Expo of ’93. At this point God created Woman as Waldo pairs up with nadara. Thus Waldo’s fears on the strand when he projected the character of a demon on this beautiful and compliant female were totally unjustified. But if Nadara represents the success that had eluded him for so long then his fears born of hysteria were warranted by his past. This is a comic novel at least at the beginning when Waldo begins his transition from the skinny, consumptive academic bookworm to that of a man of Tarzanic proportions. Thus at this stage of the book Waldo is a bumbling buffoon.
Burroughs is obviously ridiculing the Boston Transcendalist school of Ralph Waldo Emerson as Waldo’s name merely leaves off the Ralph and adds the ridiculous hyphenated Smith-Jones. The latter of course has pretensions to nobility but is compounded of the two most plebeian and common English names. Waldo’s name is as comic as Burroughs could make it. Worth a laugh or two on its own.
He may also be making a snub at his fellow students of Phillips Academy when he went East. It is well known that Easterners of the time, if not still, deprecated Westerners. Burroughs would have had to put up with much jesting and ridicule while there so perhaps he is now ridiculing those who ridiculed him.
Also he may be ridiculing his own former self.
Burroughs is fairly hostile to New England throughout his writing. He is positive on the South having more than one hero from Virginia while he is considerate of the middle states. Thus Waldo beginning as an effete New Englander will turn into something resembling John Carter/Tarzan or the Virginian of Owen Wister’s strange novel. Thus if one views Waldo in light of Burroughs three most favorite novels, The Prince And The Pauper, Little Lord Fauntleroy and The Virginian the basic tenor of all the stories is made apparent.
Waldo being pursued toward the cliff dwellings by the cave men with his legs pumping up to his chin and the stick twirling in his hand resembles a scene from a newspaper comic strip. It would seem that Burroughs was an ardent reader of the newspaper Funnies. David Innes Earth Borer was undoubtedly taken from a newspaper comic strip also. This incessant modeling or borrowing may explain a bit of the contempt for his work by contemporaries. ERB comes real close from time to time.
Having paired up with Nadara she and Waldo hold off the cave men slipping away in the night to Chapter 3, The Little Eden, which is a key chapter.
4b.
It’s A Lover’s Question
This chapter is so compacted I find it difficult to find a starting point. If Burroughs’ marriage with Emma had not run smoothly from 1900 to 1913 their relationship would become even more stressed from 1913 to 1920. The marriage apparently barely survived a major crisis c. 1918-20 finally being terminated in 1934.
The relationship of ERB and Emma is very difficult to comprehend. It seems clear that ERB had no intention of actually marrying her but wished to keep her on a string. This arrangement was doing well until Frank Martin entered the scene in 1897 or ’98. Martin forced Burroughs’ hand who was then compelled to marry Emma in 1900.
Over the years from 1900 on Burroughs developed an intense antipathy to Emma which expressed itself in its most naked form at the time of her death when ERB did everything but desecrate her grave. There must have been some deep psychological cause for this that isn’t apparent from what we know for sure of the relationship.
Perhaps the most critical event in their lives occurred on that streetcorner on the way to Brown School in the fifth grade when ERB was emasculated by John the Bully. Burroughs was then removed to the girl’s school a few months later. I have no evidence that ERB and Emma were walking to school together on that the fateful day but subsequent literary evidence points in that direction.
As a result of his emasculation it would appear that ERB was fixated in such a manner that he was unable to form relationships with women after that date and that Emma was the only female with whom he retained one. But as she reminded him of that fateful day he both rejected her and couldn’t do without her. Thus he refused to marry her yet didn’t want her to marry anyone else. When circumstances forced him to marry her this may have begun his irrational resentment toward her. As there was no other woman possible for him until the beginning of his psychological liberation in 1913 he may have tolerated her, but just.
Success seemed to liberate repressed areas of his personality and we find him dreaming of an ideal mate quite different from Jane/Emma. If one assumes that John Carter is an idealized Edgar Rice Burroughs although Burroughs projects the role of uncle on him while maintaining a dissociation from him until the end then Carter’s affiliation with Dejah Thoris on Mars would be ERB’s first Anima projection. However Dejah Thoris is more closely related to Jane. In La of Opar and Nadara Burroughs’ Anima ideal shifts more toward a wild or nature woman. This aspect of the ideal is realized in Balza, The Golden Girl of 1933 who is also represented by Florence.
So, in Cave Girl an emaciated, consumptive, over intellectualized Waldo Emerson Smith-Jones mates with the primitive Nadara who still retains the imprint of her civilized parents down by the river in the Little Eden. Thus we have Adam and Eve in the Garden before they leave never to return.
The problem of male-female relations is a dominant theme in Burroughs’ writing. Indeed the theme is one that preoccupies all writers of fiction in one degree or another. In this aspect Freud is merely a prominent writer on the sexual condition of men and women. He is perhaps more systematic but not necessarily more profound.
For instance Freud asked in a title to one of his essays What Does Woman Want and gives neither a profound nor very thoughtful answer. If he had read E.M. Hull’s 1921 novel, The Sheik, he would have have had somthing of an answer written by a woman. Burroughs did read the Sheik. He understood what Hull was saying. His answer was the major burlesque of the Alalus people of the Tarzan And The Ant Men of 1922. In this charming story of the The Cave Girl he give his 1913 answer to the question of what woman wants in a credible manner.
The answer in this case is age old. The answer was clear from ancient times to E.M. Hull’s clear story. Mostly it would appear what woman wants is a powerful protector willing to perform her will when a problem exceeds her own powers thus recompensing her for the missing X and more especially the missing y chromosome. The latter what Freud called Penis Envy. One can only conclude that woman wants to be whole, to be chomosomally undivided. Thus as a famed LA procuress once said: A woman is only as powerful as the man beside her.
Now, Nadara projects a character on Waldo as her fierce and powerful protector. As love begins in Waldo’s heart the spectre of sex arises in their little Eden in the form of the Black Panther Nagoola. Is it a coincidence that the first syllable of both names is the smae while both end in a long A? Nadara the sexual temptress.
Prompting Waldo she demands whether he could kill Nagoola. That may have a couple meanings. It may mean could he despatch the animal and it may mean can he conquer or control the sexual urge. In Waldo’s case the anwer will be yes to both questions.
He does kill Nagoola in a comedy of errors in this comic novel. In its sequel The Cave Man he will adorn Nadara with the pelt of Nagoola thus making her the physical incarnation of sexual desire. Who says Burroughs wasn’t subtle.
Too desirous of impressing Nadara as a man of prowess he allows her to think he has already killed several Nagoolas.
Very pleased to hear this she says: ‘Good. When we get to my village I want you to kill Korth and Flatfoot.’ Well now, there was a committment that Waldo had no intention of honoring, at least in his present condition.
Thus, we have a demonstration of the thesis that women are responsible for conflict. Woman proposes, man imposes.
As they can’t stay in their little Eden forever they make the trek to Nadara’s people. Waldo is committed to killing the fearsome Korth and Flatfoot. He is terrified to confront them as well he might be. As they approach the village Waldo sends Nadara ahead then legs it out of there.
Thus we have the flight or fight dilemma that is another major theme of Burroughs. At this point in his career he isn’t ready to articulate his feelings as he will later. The dilemma relates to his confrontation with John the Bully in the fifth grade. At that time as Waldo in this story Burroughs elected to run. Now, you will notice that Waldo is with Nadara which is a pretty sure indication that ERB was with Emma that fateful morning on the way to school.
In point of fact either Korth or Flatfoot would easily have killed Waldo at this stage in his career as John would have cremated the much younger Burroughs. When he would later rationalize it there is no dishonor if fleeing overwhelming force which is surely true but has its consequences.
Thus Waldo like Burroughs was sent into the Wasteland. His problem now will be to figure out how to return to kill Korth and Flatfoot to reclaim Nadara.
4c.
How Waldo Became A Man